Copy link
Nitrous Oxide
Last updated: 07/01/2024
Key Points
- Nitrous oxide is an inhaled anesthetic gas used for procedural sedation, labor analgesia, acute pain management, and as an adjunct to general anesthesia.
- Nitrous oxide acts as an anesthetic by inhibiting N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) glutamate receptors and hyperpolarizing neurons, inducing analgesia by activating opioid and noradrenergic pathways.
- Nitrous oxide is the least potent inhaled anesthetic and enhances the uptake of other inhaled anesthetic agents through the second gas effect.
- Many of nitrous oxide's adverse effects are related to its ability to expand air-filled spaces in the body and its inhibition of vitamin B12 activity.
Introduction
- Nitrous oxide is an inert, colorless, odorless gas widely used as an anesthetic or analgesic agent.
- Nitrous oxide, commonly known as laughing gas, has been used for over a century in medicine and dentistry.
Mechanism of Action
- The primary anesthetic action of nitrous oxide comes from its effects as a noncompetitive antagonist of NMDA glutamate receptors, inhibiting the excitatory glutamatergic neural signal.1
- It has secondary anesthetic action through the activation of two-pore-domain potassium channels, which has the effect of hyperpolarizing neurons.
- Nitrous oxide induces analgesia by activating opioidergic in the periaqueductal grey matter and noradrenergic neurons in the locus ceruleus.1
- Opioid release in the brainstem inhibits γ-aminobutyric acid (GABA)ergic interneurons, decreasing the inhibition of descending noradrenergic inhibitory pathways.
- Activation of locus ceruleus increases hypothalamic release of corticotropin-releasing factor, potentially creating additional NMDA receptor antagonism.
- Nitrous oxide has no direct effect on GABA receptors.1
Pharmacologic Properties
- Nitrous oxide has a minimum alveolar concentration of 104%, making it the least potent inhalational anesthetic.1,2
- It is rapidly absorbed via the lungs, with an onset of action of 2-5 minutes.3
- Nitrous oxide exhibits the second gas effect. The rapid nitrous oxide uptake from the alveoli into the bloodstream increases the concentration and accelerates the uptake of a concurrently administered second anesthetic gas, enhancing its anesthetic effect.2
- This effect reduces the required concentration of volatile anesthetics when combined with nitrous oxide, improving hemodynamic stability and decreasing respiratory depression.4
- The low blood solubility (blood/gas partition coefficient of 0.47) and low lipid solubility of nitrous oxides give it the fastest onset and washout of routinely used anesthetic agents.2,4
- Net ventilation and blood pressure are not reduced with nitrous oxide, unlike other inhalation agents.3
- Nitrous oxide does not affect skeletal muscle tone and is not associated with malignant hyperthermia.3
- Nitrous oxide is primarily eliminated through expiration and is essentially not metabolized by the body.3
- Nitrous oxide can cause increases in cerebral blood flow (CBF), cerebral metabolic rate, and intracranial pressures (ICP).2 These effects are primarily due to cerebral vasodilation and sympathoadrenal stimulation. The magnitude of these effects depends on the coadministration with other anesthetics. Nitrous oxide administered alone increases CBF and ICP. However, when intravenous anesthetics are coadministered, the cerebral-vasodilating effects of nitrous oxide are attenuated or completely inhibited. Adding nitrous oxide to inhaled anesthetics can modestly increase CBF and cerebral metabolism.2
Clinical Indications
- Nitrous oxide can be used for sedation for procedures causing mild to moderate pain (Table 1).4,5
- It can be used for procedural sedation in adult and pediatric patients.
- Anesthetic efficacy for these procedures is improved when nitrous oxide is combined with local or topical anesthetics.
- In labor analgesia, nitrous oxide effectively reduces labor pain and anxiety.4
- It can be used for the management of acute pain in emergency settings.6
- Nitrous oxide provides quick and titratable analgesia for acute pain.
- It can be an adjunct to general anesthesia. Adding nitrous oxide to general anesthesia reduces the required concentration of volatile anesthetic.4
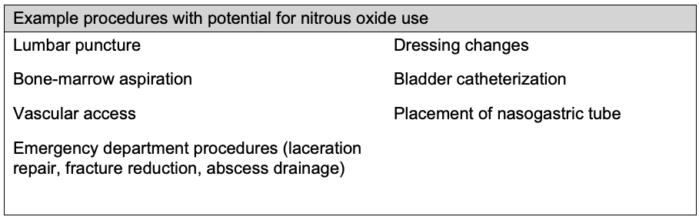
Table 1. Examples of procedures that can be performed with nitrous oxide4,5
Administration and Dosage
- Nitrous oxide is administered as a mixture with oxygen and occasionally with other anesthetic agents.
- Nitrous oxide can be given at concentrations of 20% to 70% when combined with oxygen, depending on the clinical indication (Table 2).3-6
- Nitrous oxide should never be administered without oxygen.
- The manufacturer’s labeling provides no renal or hepatic dosage adjustments.
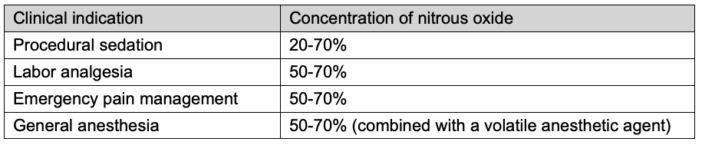
Table 2. Nitrous oxide concentrations commonly used in various clinical indications
Adverse Effects
- Nitrous oxide is 30 times more soluble in blood than nitrogen. Therefore, the use of nitrous oxide at high partial pressures can cause it to diffuse into and expand air-filled spaces in the body faster than the poorly soluble nitrogen can be carried away from the space, potentially causing harmful physiological effects such as air emboli, pneumothorax, pneumocephalus, and increased pressure in areas like the middle ear and gastrointestinal tract.2,4
- Increased pressure in the middle ear can lead to rupture of the tympanic membrane and is thought to contribute to an increased risk of postoperative nausea and vomiting.3
- Nitrous oxide irreversibly inhibits cobalamin (vitamin B12), reducing methionine synthase activity.2,3
- Chronic exposure can lead to megaloblastic anemia, myelopathy, and neuropathy, particularly in individuals with pernicious anemia or malabsorption syndromes.
- Reduced methionine synthase activity leads to increased homocysteine levels, which has been linked to vascular inflammation and atherosclerosis.2,4
- The evidence is mixed on whether nitrous oxide has effects on cardiovascular and neurovascular risk.
- The randomized ENGIMA 2 trial showed no increase in myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary embolism, or cardiac arrest with nitrous oxide use.
- Diffusion hypoxia is possible by discontinuing high nitrous oxide concentrations as the gas rapidly transfers from the blood to the alveoli.3
- Administration of 100% oxygen after nitrous oxide use minimizes this risk.
- Recreational use has been linked to chronic neurological issues, addiction, and death from asphyxia.4
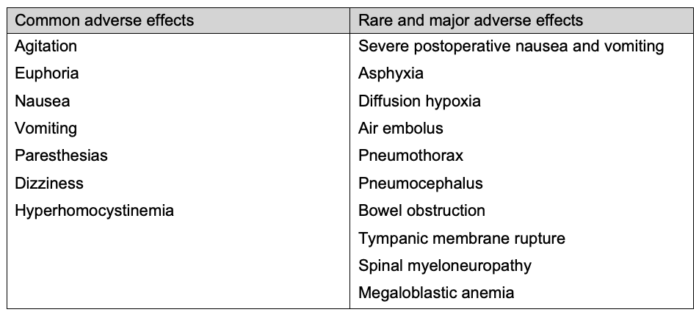
Table 3. Adverse effects of nitrous oxide2-5
Contraindications
- Unconscious or neurologically impaired patients should not receive nitrous oxide.4
- Nitrous oxide is contraindicated in patients at risk of expansion of a gas-filled space.2-4
- This includes patients with pneumothorax, pneumocephalus, elevated intracranial pressure, those at high risk for vascular air embolus, and those undergoing middle ear or retinal surgery creating an intraocular gas bubble.
- Caution should be used in patients with sinusitis.3
- Nitrous oxide is contraindicated in patients with a known deficiency in the methionine synthase pathway or those at high risk of hematologic or neurologic consequences.1,2,4
- This includes patients with known pernicious anemia, cobalamin deficiency, methyltetrahydrofolate reductase deficiency, and critically ill patients.
- Caution should be used with patients at risk for cobalamin deficiency (e.g., elderly, vegans, heavy alcohol users, postgastrectomy, Crohn’s disease).1
- Caution is advised in patients with severe psychiatric disorders.3
Breastfeeding and Pregnancy Considerations
- The use of nitrous oxide during pregnancy is considered safe.3
- Nitrous oxide does not affect oxytocin release or uterine contractions.4
- Nitrous oxide crosses the placenta but does not affect fetal heart rate, Apgar scores, or other neonatal outcomes.4
- Nitrous oxide administered to lactating patients is not expected to be absorbed by the infant due to its short serum half-life, allowing breastfeeding to resume immediately postanesthesia.7
Environmental Impact of Nitrous Oxide
• Nitrous oxide is a potential greenhouse gas and the leading cause of ozone depletion. Please see the OA summary titled “Environmental Impact of Nitrous Oxide” for more details. Link
References
- Sanders RD, Weimann J, Maze M, et al. Biologic effects of nitrous oxide: A mechanistic and toxicologic review. Anesthesiology. 2008;109(4):707-22. PubMed
- Forman SA, Ishizawa Y. Inhaled anesthetic uptake, distribution, metabolism, and toxicity. In: Gropper MA et al. (eds). Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2019: 509-539.
- Becker DE, Rosenberg M. Nitrous oxide and the inhalation anesthetics. Anesth Prog. 2008;55(4):124-132. PubMed
- Buhre W, Disma N, Hendrickx J, et al. European Society of Anaesthesiology Task Force on Nitrous Oxide: a narrative review of its role in clinical practice. Br J Anaesth. 2019;122(5):587-604. PubMed
- Gall O, Annequin D, Benoit G, Glabeke E, et al. Adverse events of premixed nitrous oxide and oxygen for procedural sedation in children. Lancet. 2001;358(9292):1514-15. PubMed
- Motov SM, Vlasica K, Middlebrook I, LaPietra A. Pain management in the emergency department: a clinical review. Clin Exp Emerg Med. 2021;8(4):268-278. PubMed
- Nitrous Oxide. In: Drugs and Lactation Database (LactMed®). Bethesda (MD): National Institute of Child Health and Human Development; February 15, 2023. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.