Copy link
Emerging Technologies: Artificial Intelligence
Last updated: 07/18/2025
Key Points
- Artificial intelligence (AI) enhances patient outcomes through early intervention, personalization, automation of routine tasks, and the use of data to elevate the standard of optimal care.
- AI optimizes anesthesiology practice by analyzing patient data to develop personalized preoperative strategies, automating anesthetic delivery, and enhancing precision in both regional anesthesiology and pain management.
- Though there are challenges (such as ethical issues, integration into current systems, and cost), future developments in wearable technology, augmented reality, adaptive learning, and collaborative AI can assist in optimizing anesthesiology care.
Introduction
- AI is being increasingly adopted in various medical specialties, including anesthesiology.
- Its incorporation into anesthesiology practice is focused on improving patient safety, optimizing anesthesia delivery, and enhancing perioperative decision-making.
Primary Applications in Anesthesiology
Automation with AI systems can improve precision, reduce human error, and assist learning for anesthesiologists in the following ways.
Perioperative Planning
- AI can analyze patient data to predict the perioperative risks and outcomes of a patient and develop a personalized preoperative plan.1
- Machine learning algorithms can predict perioperative events, such as hypotension, hypoxemia, and postoperative complications (including sepsis and nausea). Early identification enables timely interventions, which in turn improve patient outcomes and reduce the length of hospital stay.4
- AI helps to develop personalized dosing of medications based on the analysis of patient responses to different treatments.
- Closed-loop anesthesia delivery devices can automate drug administration by continuously analyzing patient parameters (heart rate and rhythm, blood pressure, and bispectral index [BIS] values), adjusting dosages in real time, thereby improving accuracy and reducing the chances of over- or under-sedation.
- Please refer to the OA summary Target Controlled Systems and Closed-Loop Systems for more details. Link
- Machine learning models can predict effective opioid dosing, minimize the possibility of addiction or overdose, and improve postoperative pain satisfaction.2,5 AI-enhanced patient-controlled analgesia systems analyze dosing patterns to adjust doses and alert clinicians to conditions of inadequate analgesia or adverse reactions.2
Monitoring
- AI can enable real-time and nonlinear dynamic brain function monitoring.
- The use of EEG signals and features, such as entropy, is shown to outperform traditional BIS monitoring in both accuracy and responsiveness.
- AI could be applied for deep learning and neural network algorithms to achieve enhanced estimation of the depth of anesthesia (Figure 1).2,3
Technology
- AI enhances ultrasound-guided regional anesthesia by identification of the anatomical landmark with accuracy as high as 95% via convolutional neural networks (Figure 1).2,3
- AI-based simulation platforms and virtual training tools can enhance the acquisition of skills in trainees. These include mannequin simulators, virtual patients, and intelligent learning platforms for better hand-eye coordination and clinical decision-making skills.2
- AI can optimize operating room schedules and workflows to enhance efficiency. Predictive algorithms estimate case durations and identify bottlenecks, hence enhancing resource allocation and reducing delays. These systems help improve the overall efficiency of perioperative care teams.6
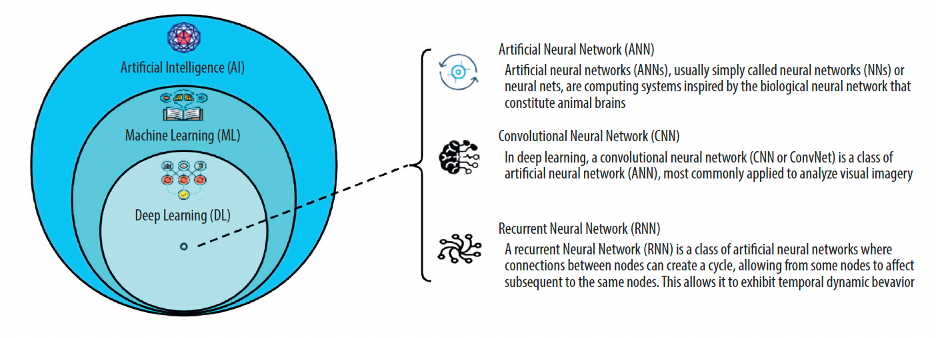
Figure 1. The relationship of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and deep learning. Source: Song B, et al. Necessity and importance of developing AI in anesthesia from the perspective of clinical safety and information security. Med Sci Monit. 2023.2 CC BY NC ND 4.0.
- Figure 2 below illustrates some of these potential applications of AI in anesthesia.
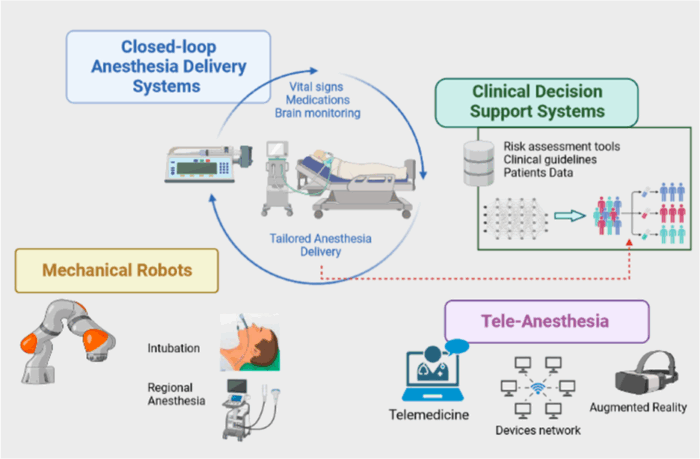
Figure 2. Infographic of potential modalities for AI-based applications in anesthesia. Source: Cascella M, et al. Exploring artificial intelligence in anesthesia: a primer on ethics and clinical applications. Preprints. 2023.8 CC BY 4.0.
Benefits
- Reduce adverse events:
- AI algorithms detect subtle physiological changes that may indicate the development of complications, enabling timely interventions.¹
- Individualized anesthesia delivery optimizes drug dosing to minimize adverse events and improve patient recovery.5
- Reduce distractions: Automating routine tasks, such as monitoring and documentation, frees the anesthesiologist for more complex clinical decision-making.6
- Identify best practices: AI identifies patterns and insights through large datasets that underpin best practices and improve the standard of care.4
Challenges and Constraints
- Privacy: AI systems need high-quality, diverse datasets to perform well. Ensuring data privacy and security is very important, especially when it comes to sensitive information about patients.5
- Complexity: The integration of AI tools into existing workflows may be complicated to some extent and may require considerable training for healthcare providers. It depends on user acceptance and seamless integration into clinical practice.8
- Bias: In the making of decisions, AI raises ethical questions about accountability and potential bias in algorithms. Fairness and transparency in applications will be key to the continued trust in the technologies.1
- Time for adoption: AI technologies also face regulatory hurdles, as they must undergo rigorous testing and approval processes to ensure safety and efficacy, which can delay implementation.6
- Cost: The development and maintenance of AI systems are expensive, thereby limiting their application, especially in resource-poor settings.5
Future Directions
- The future of AI in anesthesia is very bright, and research continues while development focuses on various aspects.
- Wearable devices that track physiological data in real-time can be used as additional inputs into AI algorithms to further enhance patient monitoring and early warning systems.8
- Combining augmented reality with AI may improve training for anesthesiologists, particularly in procedures like regional anesthesia. This synergy can enhance educational experiences and procedural accuracy.5
- The AI systems that learn and continuously improve based on ongoing clinical data could become more accurate and valuable over time.
- Such models ensure that the AI tool remains current, evolving in tandem with advancements in medical knowledge and practices.1
- Designing systems to work with, rather than replace, anesthesiologists ensures that human expertise remains central to patient care. It leverages the strengths of both AI and human judgment.6
References
- Bianco A, Al-Azzawi ZAM, Guadagno E, Osmanlliu E, Gravel J, Poenaru D. Use of machine learning in pediatric surgical clinical prediction tools: A systematic review. J Pediatr Surg. 2023;58(5):908-16. PubMed
- Song B, Zhou M, Zhu J. Necessity and importance of developing AI in anesthesia from the perspective of clinical safety and information security. Med Sci Monit. 2023;29:e938835. PubMed
- Lopes S, Rocha G, Guimarães-Pereira L. Artificial intelligence and its clinical application in anesthesiology: A systematic review. J Clin Monit Comput. 2024;38(2):247-59. PubMed
- Tremblay N, Zhang S, Cohen D, et al. Applications of Artificial Intelligence in Medicine. In: Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare. National Center for Biotechnology Information; 2023.
- Tewfik G, Naftalovich R, Kaila J, Adaralegbe A. ChatGPT and its potential implications for clinical practice: An anesthesiology perspective. Biomed Instrum Technol. 2023;57(1):26-30. PubMed
- American Society of Anesthesiologists. Is artificial intelligence the perfect fit? ASA Meeting News Central. October 2023. Link
- Bates DW, Levine D, Syrowatka A, et al. The potential of artificial intelligence to improve patient safety: a scoping review. NPJ Digit Med. 2021;4(1):54. PubMed
- Cascella M, Tracey M, Petrucci E, Bignami E. Exploring artificial intelligence in anesthesia: a primer on ethics and clinical applications. Preprints. 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.