Copy link
Nondepolarizing Neuromuscular Blocking Agents
Last updated: 11/10/2023
Key Points
- Nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA) provide skeletal muscle relaxation through competitive antagonism of acetylcholine receptors at the motor endplate.
- The onset and duration of action, associated side effects, and metabolism vary significantly among the available NMBAs.
- The onset and duration of action, associated side effects, and metabolism vary significantly among the available NMBAs.
- Atracurium and cisatracurium undergo organ-independent Hofmann elimination at physiological pH and temperature.
Overview of Muscle Contraction
- At the neuromuscular junction, motor neurons are connected to the motor endplate on individual muscle fibers via the synaptic cleft.
- Resting membrane potential of skeletal muscle is normally -90 mV with a high concentration of potassium (K+) ions inside the cell and a high concentration of sodium (Na+) ions outside the cell.
- Sodium-potassium ATPase moves K+ ions inside the cell and Na+ ions outside the cell.
- K+ ions continually move back out of the cell against their concentration gradient while Na+ channels normally remain closed creating a negative membrane potential.
- Acetylcholine (ACh) is released into the synaptic cleft as a result of an action potential and binds to nicotinic receptors on the motor endplate causing Na+ ion channels to open, allowing influx of Na+ which depolarizes the cell.
- Depolarization spreads along the sarcolemma creating an action potential which causes opening of ryanodine receptors and calcium (Ca2+) release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum.
- Ca2+ binds to troponin creating cross bridges between actin and myosin and skeletal muscle contraction.
- Acetylcholinesterase (AChE) in the synaptic cleft breaks down ACh which allows its release from the ACh receptors on the motor end plate preventing sustained muscle contraction.
- During repolarization, voltage gate Na+ channels close while K+ channels stay open causing the membrane potential to return to -90 mV.1
- Please see the OA Summary on the basics of neuromuscular blockade for more details. Link
Types of Muscle Relaxants
- NMBAs are broadly classified into two categories: depolarizing and nondepolarizing muscle relaxants.
- Depolarizing NMBAs provide skeletal muscle relaxation through direct activation of ACh receptors, while nondepolarizing agents act through competitive antagonism of ACh receptors at the motor endplate.
- This summary will focus on the nondepolarizing NMBAs.
Nondepolarizing NMBAs
- Mechanism of action: Bind to the cholinergic receptors on the motor endplate competitively antagonizing the effects of ACh and preventing depolarization and muscle contraction.
- First generation nondepolarizers (curare, gallamine, metocurine) are no longer in use.
- Based on their chemical structure, nondepolarizing NMBAs can be classified as aminosteroids and benzylisoquinoliums (Table 1).
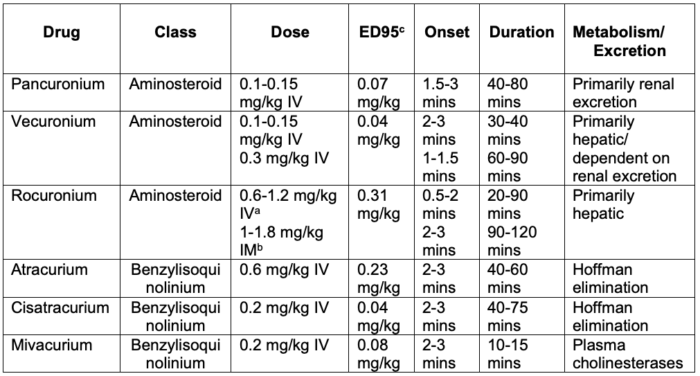
Table 1. Commonly used nondepolarizing NMBAs. Adapted from Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Morgan and Mikhail’s Clinical Anesthesiology, 7th Edition. McGraw Hill; 2022.
aDoses of 1-1.2 mg/kg IV provide intubating conditions comparable to succinylcholine for rapid sequence intubation.
bIM administration of 1 mg/kg (infants) or 1.8 mg/kg (children) produces intubating conditions in 2.5-3 minutes.
cThe amount of NMBA required to reduce twitch height by 95%
Aminosteroids tend not to cause histamine release but their metabolism is organ dependent.
- Chronic administration of anticonvulsants can lead to resistance to the effects of aminosteroid NMBAs due to stimulation of hepatic microsomal enzymes and upregulation of ACh receptors.
Pancuronium
- Dosing: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg produces intubating conditions in 90-120 seconds (0.06-0.1 mg/kg 2-3 min) with a duration of action of 40-80 minutes.
- Long-acting
- Adverse effects: Vagolytic effect may cause a transient increase in heart rate and blood pressure. This may result in atrial tachyarrhythmias.
- Elimination/Metabolism: primarily renal elimination (80%)
- Hepatic metabolism via hydroxylation to an active 3-OH metabolite (50% neuromuscular blocking effects) with dependence on renal excretion
- Chronic renal failure (CRF) increases pancuronium’s elimination half-life by 97%.
- Contraindications: renal insufficiency/failure due to prolonged duration of action
Vecuronium
- Dosing: 0.1-0.15 mg/kg results in intubating conditions in 80-90 seconds with a duration of 30-40 minutes.
- 0.3 mg/kg shortens the onset to 60-75 seconds while increasing the duration of action to 60-90 minutes.
- Intermediate-acting
- Adverse effects: Devoid of cardiovascular effects
- Metabolism: Primarily hepatic, resulting in pharmacologically active metabolites dependent on renal excretion
- The primary metabolite 3-desacetylvecuronium has 80% neuromuscular blocking activity.
- 20-30% excreted by the kidneys unchanged.
- Duration of action is prolonged in patients with liver failure and in neonates and young infants due to immature hepatic microsomal enzymes.
- Elimination half time is increased by 24-56% in patients with CRF resulting in a prolonged and variable duration of action.
Rocuronium
- Dosing: 0.6-1.2 mg/kg IV results in intubating conditions in less than 2 minutes with a duration of action of 20-90 minutes.
- Doses of 1-1.2 mg/kg provide rapid intubating conditions comparable to succinylcholine for rapid sequence induction.
- Doses of 0.3-0.45 mg/kg IV produce intubating conditions in neonates and young infants within 45-60 seconds.3
- IM deltoid administration of 1 mg/kg for infants or 1.8 mg/kg for children provides intubating conditions in 2.5 to 3 min with duration of action of 90-120 min.4
- IM administration is reserved for the treatment of laryngospasm in patients without IV access and in whom succinylcholine is contraindicated due to prolonged duration of neuromuscular blockade.
- Currently no studies address the reversal of IM rocuronium with sugammadex.
- Increased infusion requirements have been noted for prolonged infusions.
- Intermediate-acting
- Adverse effects: mild vagolytic effect
- Metabolism: primarily hepatic elimination (90% via biliary excretion) with minimal hepatic metabolism (1%) and about 10% renal excretion
- Hepatic and renal disease prolong the effects of rocuronium but to a lesser degree than with vecuronium or pancuronium.
- Elimination half time is increased by approximately 37% in CRF without significant effect on duration of action.
- Alterations in clearance are also seen in neonates and infants due to immature microsomal enzyme system; clearance rates approach adult levels by 6-12 months.
Rapacuronium
- Nondepolarizer with onset and duration is similar to succinylcholine but without associated hyperkalemia, myalgias, or MH risk.3
- It was removed from the market in 2001 due to its association with severe and potentially fatal bronchospasm.5,6
Benzylisoquinoliniums: cause histamine release to varying degrees but metabolism is organ independent
Atracurium
- Dosing: 0.6 mg/kg produces intubating conditions in 2 to 3 minutes with a duration of action of 40 to 60 minutes.
- Intermediate-acting
- Adverse effects: histamine release may cause hypotension in adult patients at larger doses. Atracurium should be avoided in asthma patients.
- Metabolism: spontaneous degradation via Hoffman elimination and ester hydrolysis
- Laudanosine (a metabolic byproduct of Hoffman elimination) has been shown to cause seizures in animals and patients with renal failure have increased levels, but no clinical effects have been documented in humans.
- Recovery time is prolonged with hypothermia as Hoffman elimination is temperature dependent.
Cisatracurium
- A stereoisomer of atracurium devoid of clinically significant histamine release or cardiovascular effects that is four times more potent.
- Dosing: 0.2 mg/kg provides intubating conditions in approximately 2 minutes.
- Intermediate-acting
- Dosing requirement increases over time with prolonged infusions.
- Recovery time is shorter after cisatracurium infusion when compared with vecuronium.
- Metabolism: Hoffman elimination
- As with atracurium, laudanosine is a byproduct and hypothermia prolongs recovery time.
Mivacurium
- Dosing: 0.2 mg/kg produces intubating conditions in 2 to 3 minutes with a duration of around of 10 minutes.
- The shortest acting of the nondepolarizers
- Adverse effects: Mivacurium can cause histamine release.
- It was unavailable in the United States from 2006-2016.
- It does not require reversal with neostigmine and may be use useful in patients with neuromuscular disorders due to its short duration of action.
- Metabolism: Nonspecific plasma cholinesterase
- Inactive metabolites are renally excreted.3
- Acquired or congenital deficiencies of butyrylcholinesterase can cause prolonged blockade similar to succinylcholine.7
- As with succinylcholine, mivacurium should be avoided in patients with a personal or family history of pseudocholinesterase deficiency.
References
- Gash MC, Varacallo M. Physiology, Muscle Contraction. In: StatPears (Internet). Treasure Island (FL); StatPearls Publishing; 2023. PubMed
- Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD. Neuromuscular blocking agents. In: Morgan and Mikhail’s Clinical Anesthesiology, 7th Edition. McGraw Hill; 2022.
- Tobias JD. Neuromuscular blocking agents. In: Fuhrman BP, Zimmerman JJ (eds). Fuhrman & Zimmerman’s Pediatric Critical Care. Elsevier; 2022. 1567-82.
- Reynolds LM, Lau M, Brown R, et al. Intramuscular rocuronium in infants and children. Dose ranging and tracheal intubation conditions. Anesthesiology. 1996;85(2):231-9. PubMed
- Tobias JD, Johnson JO, Sprague K, et al. Effects of rapacuronium on respiratory function during general anesthesia. Anesthesiology. 2001;95(4):908-12. PubMed
- Rajchert DM, Pasquariello CA, Watcha MF, et al. Rapacuronium and the risk of bronchospasm in pediatric patients. Anesth Analg. 2002;94(3):488-93. PubMed
- Rosenberg MK, Lebenbom-Mansour M. Markedly prolonged paralysis after mivacurium in a patient apparently heterozygous for the atypical and usual pseudocholinesterase alleles by conventional biochemical testing. Anesth Analg. 1997;84(2):457-60. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.