Copy link
Tocolytics and Uterotonics
Last updated: 02/14/2024
Key Points
- Autoregulation of uterine blood flow is lost during pregnancy, and blood flow depends on uterine perfusion pressure and uterine vascular resistance (tone).
- Halogenated inhalational agents cause dose-dependent depression of uterine contractility. Commonly used intravenous (IV) anesthetic agents and nitrous oxide have minimal or no direct effects on uterine tone.1
- Uterotonic medications can be used to augment uterine tone and decrease postpartum blood loss.
Introduction
- The uteroplacental circulation delivers oxygen and nutrients essential for the growth and development of the fetus and placenta. Acute reductions in uteroplacental blood flow impact placental perfusion and may rapidly threaten fetal viability.
- Uteroplacental blood flow increases dramatically during pregnancy, reaching approximately 900 mL/min and representing about 12% of the maternal cardiac output.
- The uterine arteries primarily supply blood flow to the uterus (~85%), with minor contributions from the ovarian arteries (~15%).1
- Uterine blood flow is proportional to uterine perfusion pressure and inversely proportional to uterine vascular resistance.
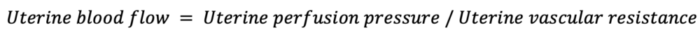
- During pregnancy, uterine autoregulation is lost, and uteroplacental circulation becomes a low-resistance system with perfusion that is largely pressure-dependent.1
- With the onset of labor, uteroplacental perfusion becomes cyclical. Contractions result in a decrease in flow proportional to the strength of contraction and an increase in intrauterine pressure. The opposite occurs during uterine relaxation.
Effects of Anesthetic Agents on Uterine Tone
The effects of anesthetic agents on uterine tone are listed in Table 1.

Table 1. Effects of anesthetic agents on uterine tone
Nonanesthetic Uterine Relaxants
- Commonly used nonanesthetic uterine relaxants are listed in Table 2.

Table 2. Commonly used nonanesthetic uterine relaxants
Tocolytics for Preterm Labor
- Commonly used tocolytics for preterm labor are listed in Table 3.
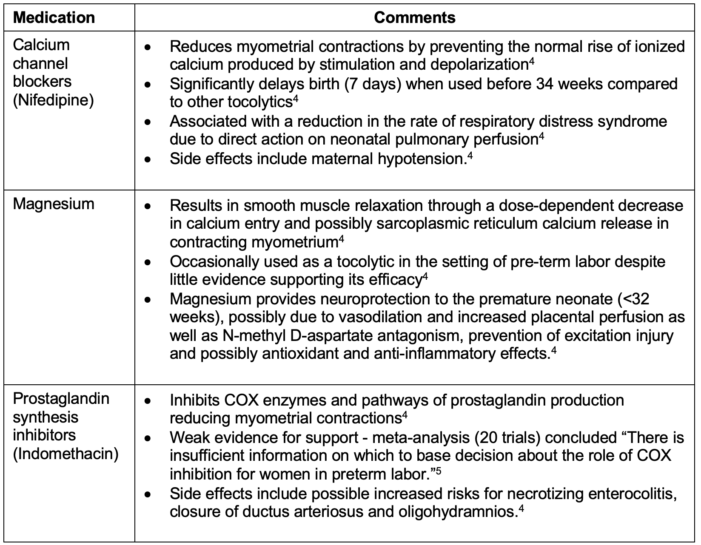
Table 3. Commonly used tocolytics for preterm labor
Postpartum Hemorrhage and Uterotonic Agents
- Postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) is the leading cause of maternal mortality worldwide. In the United States, it accounts for 11.4% of maternal deaths and is the leading cause of maternal intensive care unit admissions.6
- The number one cause of PPH is uterine atony, accounting for approximately 80% of cases.7
- Uterine contraction is the primary mechanism for controlling blood loss at parturition. Endogenous oxytocic substances are released after delivery, resulting in a shearing force that cleaves the placenta from the uterine wall and causes constriction of the spiral arteries and placental veins supplying the placenta. Uterine atony represents a failure of this process.
- Uterotonic medications can be used to augment uterine tone and decrease blood loss as a result of poor uterine tone. The American College of Obstetrics and Gynecology recommends active management of the third stage of labor, including uterine massage and prophylactic oxytocin administration to decrease blood loss and transfusion requirements, compared to expectant management.8
- Commonly used uterotonic agents are listed in Table 4.
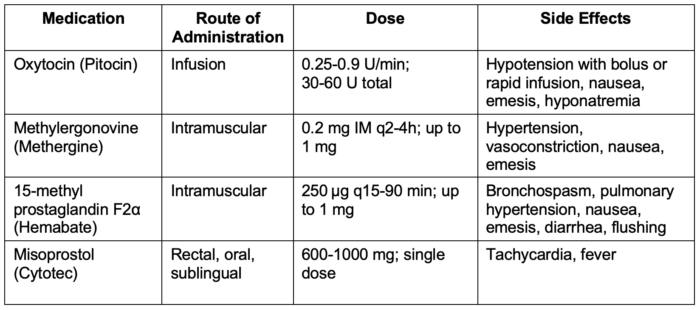
Table 4. Commonly used uterotonic agents
Oxytocin
- First-line drug for the management of uterine atony after delivery of a third-trimester pregnancy (the number of high-affinity receptors for oxytocin increases greatly near term; alternative uterotonics are more effective in the first and second trimesters of pregnancy).3
- Endogenous oxytocin is produced in the posterior pituitary gland. The exogenous form (Pitocin, Syntocinon) is a synthetic peptide with rapid action and short half-life.
- Side effects include vasodilation, tachycardia, hypotension, coronary vasoconstriction, myocardial ischemia, and rarely, death. Adverse effects are typically dose-related, and phenylephrine can mitigate the adverse hemodynamic changes. Dosing is variable, but 0.25–0.9 IU/min is generally administered via an IV infusion.3
Ergot Alkaloids (Methylergonovine and Ergonovine)
- Methylergonovine is a semisynthetic ergot alkaloid that rapidly produces tetanic uterine contraction.
• The mechanism of action is poorly understood, but the uterotonic effect is most likely mediated by serotonergic agonism. Typically administered intramuscularly (IM) with a quick onset of action and uterotonic effects lasting 2-4 hours.3 - Parenteral administration is associated with a high risk of nausea and vomiting, and IV administration is avoided due to the high risk of serious cardiovascular system derangements.3
- Adverse effects are rare but include vasoconstriction, hypertension, myocardial ischemia and infarction caused by coronary vasospasm, cerebrovascular accident, seizures, and death. Relative contraindications include hypertension, preeclampsia, peripheral vascular disease, and ischemic heart disease. Dosing is 0.2 mg IM.3
Prostaglandins (E and F Families)
- Increase myometrial intracellular free calcium concentration, increasing myosin light-chain kinase activity and uterine contraction.
- Endogenous concentrations increase during labor and peak at the time of placental separation. Common side effects include fever, chills, diarrhea, nausea, and vomiting.3
15-Methyl Prostaglandin F2α (Hemabate)
- A dose of 0.25 mg (250 µg) is typically given IM. Dosing can be repeated every 15-30 minutes and should not exceed a total of 2 mg.3
- Relative contraindications include reactive airway disease, pulmonary hypertension, and hypoxemia due to the increased risk for bronchospasm, abnormal ventilation-perfusion ratio, and increased intrapulmonary shunt fraction.3
- It is likely a less effective second-line uterotonic when compared to methylergonovine.3
Misoprostol
- Prostaglandin E1 analog used for cervical ripening and induction of labor.
- Not as effective as oxytocin, but prophylactic administration reduces the incidence of PPH in patients who do not receive oxytocin.3
- It is likely the least effective second-line uterotonic.3
- It does not require IV access for administration and can be stored at room temperature, making it ideal for use in under-resourced areas.
- Typical dosing is 600 to 1000 µg. Routes of administration include buccal (recommended), sublingual, vaginal, or rectal.3
References
- Ngan Kee, W. Uteroplacental blood flow. In: Chestnut DH, Nathan N. Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. Sixth edition. Philadelphia; Elsevier; 2020: 38-49.
- Tsen L, Bateman B. Anesthesia for cesarean delivery. In: Chestnut DH, Nathan N. Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. Sixth edition. Philadelphia; Elsevier; 2020: 568-612.
- Banayan, J, Hofer, J, and Scavone, B. Antepartum and postpartum hemorrhage. In: Chestnut DH, Nathan N. Chestnut’s Obstetric Anesthesia: Principles and Practice. Sixth edition. Philadelphia; Elsevier; 2020: 901-28.
- Arrowsmith S, Kendrick A, Wray S. Drugs acting on the pregnant uterus. Obstet Gynaecol Reprod Med. 2010;20(8):241-247. PubMed
- Reinebrant HE, Pileggi-Castro C, Romero CL, et al. Cyclo-oxygenase (COX) inhibitors for treating preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2015;2015(6):CD001992. PubMed
- Creanga AA, Syverson C, Seed K, Callaghan WM. Pregnancy-related mortality in the United States, 2011-2013. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(2):366-373. PubMed
- Bateman BT, Berman MF, Riley LE, Leffert LR. The epidemiology of postpartum hemorrhage in a large, nationwide sample of deliveries. Anesth Analg. 2010;110(5):1368-73. PubMed
- Committee on Practice Bulletins-Obstetrics. Practice Bulletin No. 183: Postpartum Hemorrhage. Obstet Gynecol. 2017;130(4):e168-e186. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.