Copy link
Myasthenia Gravis
Last updated: 03/08/2024
Key Points
- Myasthenia gravis (MG) reduces postsynaptic proteins (typically acetylcholine receptors) at the neuromuscular junction (NMJ), causing fluctuating muscle weakness and unique sensitivities to neuromuscular blocking agents (NMBA).
- A patient’s recent course of MG, affected muscle groups, drug therapy, and concomitant diseases are important anesthesiology considerations.
- Stressors such as surgery or recent illness can exacerbate MG symptoms and induce a myasthenia crisis, a life-threatening condition.
Introduction
- MG is the most common NMJ disorder and is characterized by skeletal muscle weakness and fatigue that worsens with repeated use.1,2
- MG is caused by the autoimmune-mediated destruction of acetylcholine receptors at the postsynaptic membrane of the NMJ.
- Anesthetic concerns for MG patients revolve around interactions between the disease pathophysiology, MG treatment, and anesthetic medications, with a specific concern regarding the use of NMBA drugs.3-5
- Respiratory muscle function, MG pharmacotherapy, and history of disease course are critical risk factors for postoperative respiratory failure.3-5
- Differentiating a cholinergic crisis from a myasthenic crisis in a MG patient with postoperative neuromuscular respiratory failure is essential for proper treatment.5
Pathophysiology
- Weakness in MG is caused by the autoimmune-mediated loss of postsynaptic proteins of the NMJ.
- Approximately 85% of patients have autoantibodies against nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs) on the postsynaptic membrane of the NMJ, though antibodies directed toward other synaptic proteins may also be present (MuSK, LRP4, agrin, or titin).1,2
- Antibodies against nAChRs pathologically block acetylcholine (ACh) from binding to nAChR and incite complement-mediated nAChR destruction, leading to a reduction of nAChR activation at the NMJ.1,2
- Loss of ACh action at the postsynaptic membrane of the NMJ produces reduced motor end-plate potential (MEPP) amplitude, diminished miniature MEPP amplitude, and failure to initiate muscle fiber contraction.1
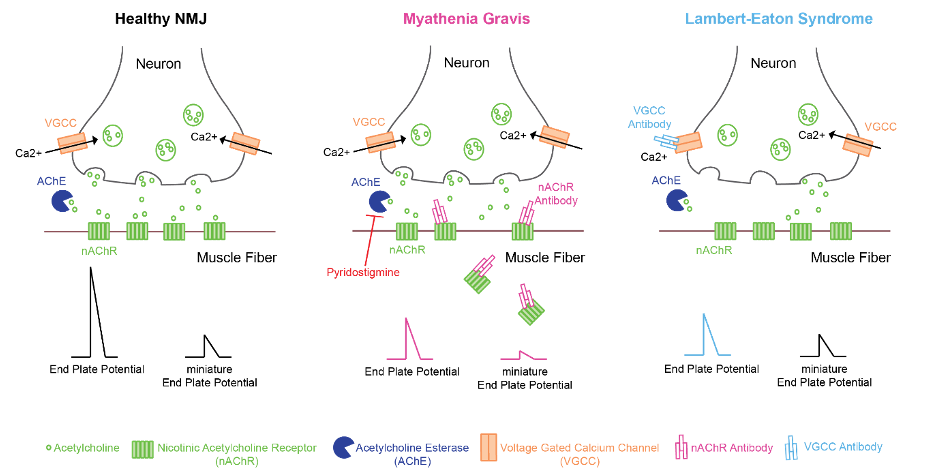
Figure 1. Pathophysiology of myasthenia gravis and Lambert-Eaton syndrome
Clinical Presentation
- MG clinically manifests as painless skeletal muscle weakness that worsens with sustained use and improves with rest. The typical course of MG is characterized by cycles of exacerbations and remissions of symptoms.
- Initially, MG symptoms are often limited to the eyelids and extraocular muscles (ocular MG), but most patients will progress to involve limb, bulbar, and respiratory muscles within 3 years (generalized MG).1,2
- Approximately 75% of MG patients have abnormal thymus glands (85% have hyperplasia, 15% show thymoma) which contributes to general immune dysfunction.1,2
- An MG diagnosis is confirmed by the presence of serum anti-nAChR antibodies in most patients. Seronegative patients undergo further neurophysiological and/or pharmacological testing of effected muscles.1
- Neurophysiological testing shows decreased compound muscle action potentials on EMG repetitive stimulation or increased jitter on single-fiber EMG.
- Historically, the tensilon test was used and involved the administration of a short, rapid-acting acetylcholinesterase inhibitor (edrophonium or neostigmine). Patients with MG usually demonstrate marked clinical improvement. This test is typically no longer used due to safety hazards of drug-induced bradycardia.1,2
- Chest imaging (CT, MRI) may be performed to evaluate for a thymoma.
Treatment
- Medical Therapy
- Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors (e.g., pyridostigmine) are used for symptomatic management to increase the amount of ACh at the NMJ.1,2
- Chronic immunosuppression with steroids (e.g., prednisone) is often prescribed additionally to reduce general autoimmune dysfunction.1,2
- Plasmapheresis or intravenous immunoglobulins (IVIG) may be used in severe cases for hospitalized patients.1,2
- Surgical Therapy
- Surgical thymectomy is used for long-term immunomodulation in patients with thymus gland abnormalities. Post thymectomy, approximately 75% of patients achieve remission or have improved symptoms.1,4,2
Anesthetic Considerations
- Patients with generalized MG have weakened respiratory muscles and unique sensitivities to NMBA drugs, deeming them at risk for aspiration and requiring thoughtful pharmacotherapy plans.3-5
- When possible, local or regional anesthesia should be considered for MG patients though care should be applied to avoid further paralysis of respiratory muscles (high-spinal anesthesia or diaphragm paralysis with brachial plexus blocks).
- In general, the use of short-acting sedative and anesthetic agents is preferred to lessen the amount of respiratory depression that occurs on emergence from anesthesia.1-5
Preoperative Evaluation
- Preoperative considerations are tailored to the patient’s recent disease course and current drug therapies. The goal is to minimize muscle weakness exacerbation and preserve respiratory function.2
- Preoperative consultation with the patient’s neurologist should be considered.
- When possible, elective surgeries should be performed when MG patients are in remission. Ideally, surgical procedures should be scheduled in the morning when these patients have peak muscle function.
- In addition to obtaining the standard preoperative history and physical examination, MG patients should be evaluated for the following:
- Bulbar symptoms and/or respiratory weakness that increases the risk for aspiration and/or respiratory failure3
- History of a myasthenic crisis (or prior need for prolonged endotracheal intubation)
- Associated diseases (e.g., secondary autoimmune diseases)
- Current medications patient is taking to treat MG
- Premedication with opioids, benzodiazepines, and barbiturates should be avoided due to depressed respiratory function in many MG patients.
- MG patients should be continued on their anticholinesterase medication through the morning of surgery to prevent additional respiratory and bulbar weakness.1
- MG patients should also be continued on their daily glucocorticoid dose.1
- Preoperative evaluation of hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis function should be considered in patients taking 5 mg or greater of prednisone (or its equivalent) for >3 weeks within 6 months of surgery or who appear Cushingoid. The need for stress dose glucocorticoid administration should be evaluated before anesthesia induction in these patients.
Intraoperative Considerations
Monitoring
- A peripheral nerve stimulator or preferably, a quantitative neuromuscular blockade monitor (e.g., EMG, accelerometer, kinemyography) should be used to record baseline responses.
- At baseline, MG patients can have a fade in response to train-of-four and tetanic stimulation in the affected muscles.1,2
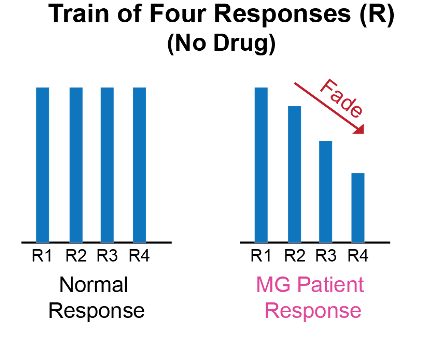
Figure 2. Train-of-four response in MG patients
Induction & Maintenance
- Induction and maintenance of general anesthesia can be achieved with inhalational (e.g., sevoflurane) and/or intravenous agents (e.g., propofol).
- The potential exists for inhalational agents to cause a dose-dependent neuromuscular relaxation in MG patients.
- The use of NMBA should be avoided, if possible, due to the reduced functional postsynaptic nAChR at the NMJ in MG patients. MG patients are exquisitely sensitive to nondepolarizing NMBA (e.g., rocuronium) and are resistant to depolarizing NMBA (e.g., succinylcholine).1,5
- MG patients are at an elevated risk for developing phase II neuromuscular block when administered succinylcholine.
- If NMBA use cannot be avoided, rocuronium in reduced (and incremental) doses should be used and its effects should be reversed with sugammadex. If sugammadex is not available, the use of NMBA should be avoided, if at all possible.1
- NMBA reversal with an anticholinesterase reversal drug (e.g., neostigmine) can induce a cholinergic crisis in MG patients. Development of muscarinic symptoms such as lacrimation, increased salivation, diarrhea, and blurry vision raise suspicion for a cholinergic crisis.
Postoperative Management
- Postoperative considerations for MG patients are centered around predicting the patient’s need for continued intubation or other ventilator support (Table 1).1-2
- MG patients are at an elevated risk for developing respiratory failure after general anesthesia. Evaluating the predictive factors below guides the patient’s postoperative plan.
- Postoperative evidence of tachypnea, respiratory acidosis, or a vital capacity <8 mL/kg is suggested criteria for reintubation.2
- Postoperative respiratory distress in MG patients may be caused by an overdose of anticholinergic medication (i.e., cholinergic crisis) or decreased response to anticholinergic medication from surgical stress (i.e., myasthenia crisis). These causes can be delineated through the tensilon test (a.k.a., edrophonium test) which causes symptomatic improvement in a myasthenia crisis.1
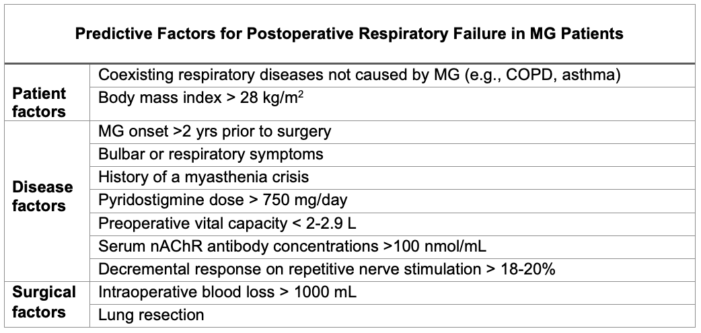
Table 1. Predictive factors for postoperative respiratory failure in MG patients
Myasthenia Crisis
- An acute exacerbation of myasthenic symptoms can be incited by infection, surgery, pregnancy, childbirth, medications, and reducing immunosuppressive medications but also occurs spontaneously.1
- A myasthenia crisis includes respiratory failure caused by severe respiratory muscle weakness that is often complicated by bulbar weakness and can be life-threatening.3
- The clinical presentation of a myasthenia crisis includes dyspnea that worsens when supine, dysphagia with a weakened cough, and generalized signs of respiratory muscle weakness.
- Patients in a myasthenic crisis have a low baseline vital capacity (<30 mL/kg of ideal body weight) and maximal inspiratory pressure below 1/3 of normal.1
- A myasthenic crisis should be managed in the intensive care unit with emergent elective intubation or noninvasive ventilation, rapid plasma exchange or intravenous immune globulin, and high-dose glucocorticoids.
Obstetric Considerations and Neonatal Myasthenia
Obstetric Considerations
- Pregnant MG patients should have an antepartum consultation that includes a similar preoperative evaluation as surgical MG patients, such as degree of bulbar involvement.
- Pregnant MG patients should have predetermined plans for labor analgesia, instrumented delivery anesthesia, and cesarean delivery anesthesia.1
- For labor analgesia, neuraxial analgesia is preferred to avoid or reduce the use of opioids which can cause excessive respiratory depression in MG patients with weakened respiratory muscles.1
- MG patients may experience difficulty during the second stage of labor where striated muscle use is required, which may indicate the use of instrumented delivery. Neuraxial analgesia is the preferred analgesia for instrumented delivery in these patients.1
- During a cesarean delivery, the midthoracic level and amount of neuraxial anesthesia required often impacts accessory respiratory muscles and may not be tolerated in MG patients. MG patients with significant bulbar involvement should undergo general anesthesia for cesarean delivery.1
Neonatal Myasthenia Gravis
- After delivery, transient neonatal MG can occur from placental transfer of maternal antibodies (anti-AChR) in 10-20% of infants from mothers with MG.1
- Neonatal MG manifests as feeding difficulties and respiratory dysfunction.
- Neonatal MG is managed by acetylcholinesterase inhibitors, but is transient and usually only requires temporary treatment.
- The risk of reoccurrence with subsequent pregnancies in mothers with MG is 75%.1
- Congenital MG can also occur via a variety of genetic defects in the protein components of the NMJ that is not autoimmune-mediated.
- Congenital MG presents as motor weakness, ophthalmologic symptoms, and respiratory difficulties.
- Similar anesthetic considerations are taken with neonate MG patients such as resistance to depolarizing NMBA, high sensitivity to nondepolarizing, high susceptibility to opioid-induced respiratory depression, and increased risk for requiring postoperative ventilation.
Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome
- Lambert-Eaton Myasthenic Syndrome (LEMS) is an uncommon NMJ disorder that causes muscle weakness that improves with repeated exercise.
- Muscle weakness in LEMS typically starts in the proximal legs and causes difficulty walking, with minimal ocular or bulbar muscle involvement. Rarely, LEMS results in respiratory failure.
- In LEMS, muscle weakness is caused by autoimmune-mediated destruction of presynaptic voltage-gated calcium channels resulting in reduced ACh release at the NMJ.1
- Reduced presynaptic ACh release with preserved postsynaptic nAChR function at the NMJ causes reduced MEPP amplitudes and normal miniature MEPP amplitudes.
- Approximately 60% of LEMS patients have an underlying malignancy, most commonly small-cell lung cancer, which then classifies LEMS as a paraneoplastic syndrome.1
- Autonomic dysfunction is commonly seen in LEMS patients with underlying malignancies.
- LEMS is treated by addressing the underlying malignancy and shows significant symptomatic improvement after the administration of drugs that increase presynaptic acetylcholine release (e.g., guanidine hydrochloride, 3,4-dyaminopyradine).1
- Many of the same anesthetic considerations and principles for MG patients apply to patients with LEMS, though a main difference is that LEMS patients are sensitive to both depolarizing and nondepolarizing NMBAs.
References
- Kveraga R, Pawlowski J. Anesthesia for the patient with myasthenia gravis. In: Post T: UpToDate. 2024. Accessed 1/17/2024. Link
- Eisenkraft JB, Samuelson S. Myasthenia Gravis. In: Yao FSF. Yao & Artusio’s anesthesiology: problem-oriented patient management. 8th Edition. Philadelphia; Wolters Kluwer; 2016: 991-1000.
- Leventhal SR, Orkin FK, Hirsh RA. Prediction of the need for postoperative mechanical ventilation in myasthenia gravis. Anesthesiology. 1980; 53:26-30. PubMed
- Watanabe A, Watanabe T, Obama T, et al. Prognostic factors for myasthenic crisis after transsternal thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2004; 127:868-76. PubMed
- Lee HS, Lee HS, Lee HE, et al. Predictive factors for myasthenic crisis after videoscopic thymectomy in patients with myasthenia gravis. Muscle Nerve. 2015; 52:216-20. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.