Copy link
Peripheral Nerve Injuries from Positioning
Last updated: 11/10/2023
Key Points
- The incidence of peripheral nerve injury (PNI) after general anesthesia is less than 1% but represents approximately 22% of general anesthesia malpractice claims from 1990-2007.
- Injuries to the brachial plexus and ulnar nerves represent two-thirds of PNI claims.
- Stretching, compression, ischemia, and inflammation are the potential causes of perioperative PNI.
- Constant vigilance is important during the preoperative and intraoperative stages of anesthesia to decrease the risk of development of perioperative PNI.
Introduction
- PNI represented 22% of cases in the 1990 to 2007 American Society of Anesthesiologists’ Closed Claims Project and are second to death as the leading cause of claims against anesthesiologists.
- Definition: Perioperative PNI is defined as “postoperative signs and symptoms related to PNI (may include but are not limited to paresthesias, muscle weakness, tingling, or pain in the extremities).”1
- Anatomy:
- Peripheral nerves are composed of bundles of fibers within multiple layers of connective tissues. The endoneurium wraps around the axons and is then bundled into fascicles by the perineurium. Blood is supplied to the peripheral nerves by the vasa nervorum, a delicate capillary network in the endoneurium (Figure 1).
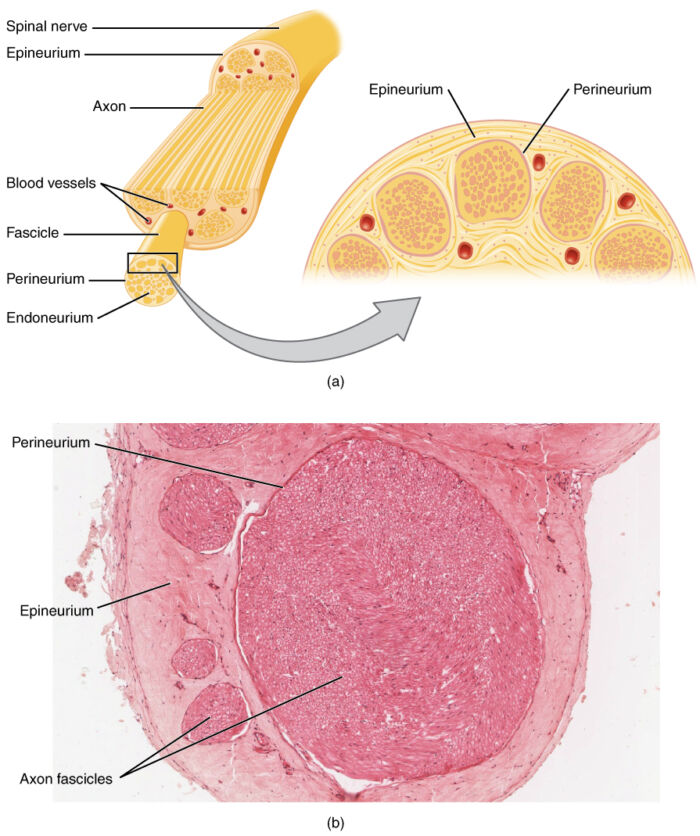
Figure 1. Anatomy of a peripheral nerve. Source: Wikimedia Commons. OpenStax College. CC BY 3.0. Link.
- Mechanisms of PNI
- PNI may be multifactorial and may be caused by a combination of local and systemic insults (e.g., stretching, ischemia, compression, or inflammation) (Figure 2).
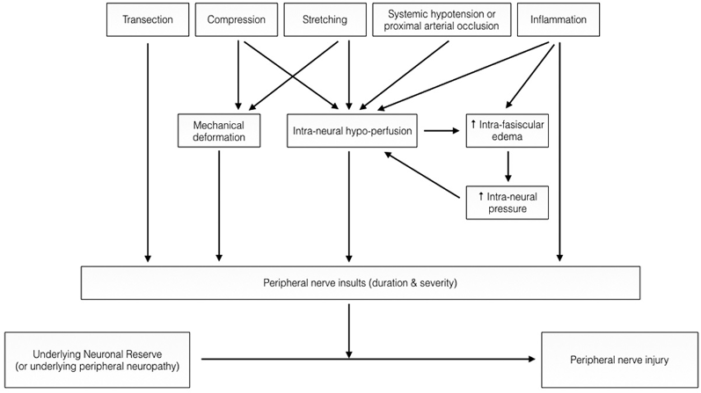
Figure 2. Pathophysiology of PNI. Used with permission from Chui J, et al. Perioperative peripheral nerve injury after general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2018. Link.
- Classification of PNI
- Two classification systems have previously been described in the literature (Table 1).
- Seddon’s classification divides PNI into three groups based on nerve pathology: neurapraxia, axonotmesis, and neurotmesis.
- Sunderland’s classification divides PNI into five groups based on which connective tissue components are disrupted: first through fifth degrees.
- Two classification systems have previously been described in the literature (Table 1).
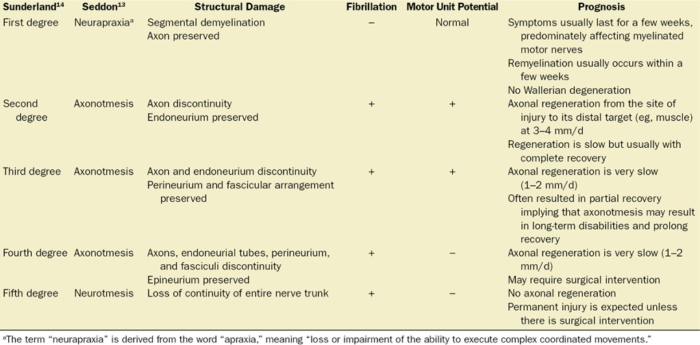
Table 1. Types of PNIs and corresponding prognosis. Used with permission from Chui J, et al. Perioperative peripheral nerve injury after general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2018. PubMed.
Predisposing Factors
- Patient characteristics reported to be associated with perioperative neuropathies:4
- Hypertension
- Diabetes
- Vascular disease
- Older age
- Extremes of weight (thin and obese body habitus)
- Heavy alcohol and tobacco use
- Male gender
- Hypotension, hypovolemia, dehydration
- Coagulopathy or presence of hematoma near nerve
- Infection/abscess near nerve
- Preexisting generalized neuropathy
- Hereditary predisposition
- Structural/congenital anomaly
- Hypothermia
- Procedural risk factors
- Cardiac, neurosurgery, and some orthopedic procedures
- General and epidural anesthesia
- Prolonged surgical times
Upper Extremity Nerve Injuries
- Ulnar nerve injuries
- Most common of all positioning-related injuries2
- Approximately 40% of sensory-only ulnar neuropathies resolve within 5 days, 80% resolve within 6 months.
- Few sensorimotor neuropathies resolve within 5 days, 20% resolve within 6 months, most result in permanent motor dysfunction and pain.
- The ulnar nerve is anatomically susceptible due to its path within the ulnar groove.
- Men are more susceptible to injury because of a more developed and thickened flexor retinaculum, less protective adipose tissue, and a larger tubercle of the coronoid process.
- Most common of all positioning-related injuries2
- Median nerve injuries
- The median nerve is much less susceptible than the ulnar nerve.
- Isolated median nerve injuries most commonly occur from direct nerve injury during intravenous catheter insertion in the antecubital fossa.
- Damage may also result from overextension of the elbow past the patient’s comfort (would need to assess preoperatively).
- The median nerve is much less susceptible than the ulnar nerve.
- Brachial Plexus injuries
- There are two patterns of brachial plexus injuries.
- Classic postoperative brachial plexus injury
- Occurs typically during hyperextension of the shoulder (e.g., steep Trendelenburg or when the arm is abducted more than 90 degrees)
- Poststernotomy brachial plexus injury
- Occurs typically after cardiac surgery associated with retractors and surgical technique.
- There are two patterns of brachial plexus injuries.
- Radial nerve injuries
- The radial nerve travels in the spiral groove of the humerus, and thus, damage would most likely result from compression of the nerve between the operating table and the humerus.
Lower Extremity Nerve Injuries
- Peroneal nerve injuries
- The peroneal nerve courses over the fibular head, and thus, is prone to injury when this area is not appropriately padded.
- Sciatic nerve injuries
- Rare (0.2%-0.3% after vaginal surgeries)
- The sciatic nerve and its branches cross both the hip and knee joints, and thus, excessive extension and flexion of these joints may increase the risk of injury.
- Femoral nerve injuries
- More commonly injured from lower abdominal surgical procedures with excessive traction but may also result from overextension or overflexion of the hip.
- Femoral neuropathy may present as decreased hip flexion, decreased knee extension, or loss of sensation over the superior aspect of the thigh and medial or anteromedial side of leg.
- Obturator nerve injuries
- Also commonly injured from excessive traction in lower abdominal surgeries
- Presents as an inability to adduct the leg and decreased sensation to the medial thigh
- Lateral femoral cutaneous nerve
- The lateral femoral cutaneous nerve is at increased risk in the lithotomy position.
Perioperative Management
- Preoperative assessment1
- A focused preoperative history should be obtained to identify patients at an increased risk.
- Prior to induction of general anesthesia, whether the patients can comfortably tolerate the anticipated operative position should be ascertained when appropriate.
- Intraoperative considerations1
- Proper patient positioning is critical to prevent PNIs (Table 2).
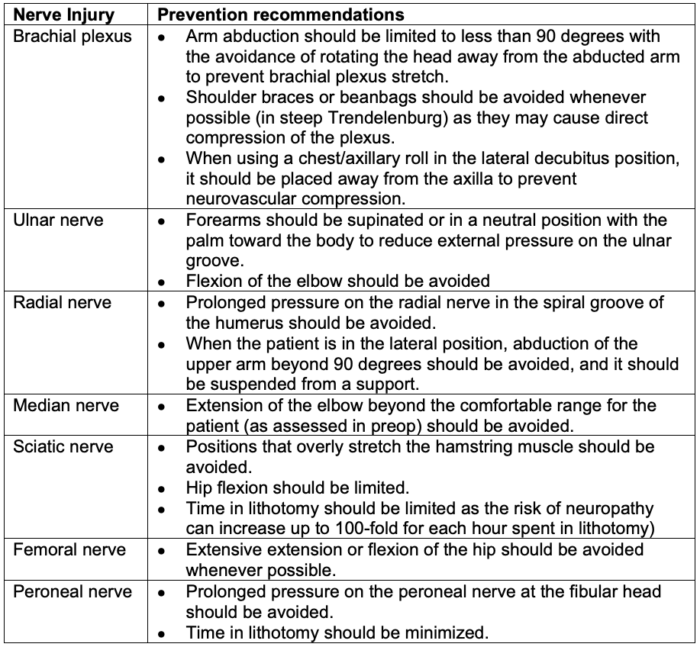
Table 2. Position recommendations to prevent PNI.3
-
- Protective padding
- Padding the elbow too tightly can paradoxically cause injury. The goal of padding is to distribute weight over as wide an area as possible.
- Periodic assessment and documentation are essential.
- Continual nerve monitoring in selected high-risk patients and procedures should be considered.
- Somatosensory evoked potential (SSEP) monitoring may be considered; however, the diagnostic accuracy and efficacy of SSEP in decreasing the risk of PNI is still unclear.
- Protective padding
- Postoperative considerations4
- A thorough postoperative assessment (a full history and exam) is important for early recognition of PNI.
- Proper documentation of findings and early neurologist evaluation is imperative.
- Progressive and severe nerve pathology requires urgent neurologist assessment and investigation.
- Key diagnostic tests: Nerve conduction studies (NCS) and needle electromyography can confirm diagnosis, localize injury, classify degree, predict prognosis, and may direct surgical intervention.2
- NCS can localize PNI in the first 7 days. Though many neurologists withhold investigation until 3-4 weeks after the injury because most diagnostic and prognostic information can be obtained in a single study.
- Electrodiagnostic tests at 3-4 weeks after surgery can distinguish the severity of PNI.
- Follow-up study in 3-6 months can provide information regarding reinnervation.
- A thorough postoperative assessment (a full history and exam) is important for early recognition of PNI.
References
- Practice Advisory for the prevention of perioperative peripheral neuropathies 2018: An updated report by the American Society of Anesthesiologists task force on prevention of perioperative peripheral neuropathies. Anesthesiology 2018; 128:11–26. PubMed
- Chui J, Murkin JM, Posner KL, et al. Perioperative peripheral nerve injury after general anesthesia. Anesth Analg. 2018;127(1):134-143. PubMed
- Breyer K and Roth, S. Chapter 32: Patient Positioning and Associated Risks. Miller RD. Miller’s Anesthesia. 8th ed. Elsevier/Saunders; 2015: 1080-97.
- Webster K. Peripheral nerve injuries and positioning for general anaesthesia. Anesthesia Tutorial of the Week. WFSA. Accessed July 12th, 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.