Copy link
Magnesium in Pregnancy
Last updated: 09/20/2023
Key Points
- Intravenous (IV) magnesium can be used in obstetric practice for seizure prophylaxis in parturients with eclampsia and preeclampsia with severe features and can also be used for fetal neuroprotection in pregnancies less than 30-weeks gestation.1
- Patients on magnesium infusions should be frequently monitored for signs of hypermagnesemia, such as loss of patellar reflexes.
- Magnesium can prolong nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockade, which can have significant effects during general anesthesia.
Indications for Use
Seizure Prophylaxis
- Magnesium is the most effective agent in preventing recurrent seizures in parturients with eclampsia and for seizure prophylaxis in those with preeclampsia with severe features.2
- Magnesium is not indicated in preeclampsia without severe features.
Fetal Neuroprotection
- Antenatal magnesium should be given to women at risk of preterm birth (from viability to 30 weeks) to reduce the risk of cerebral palsy in the child and also to reduce the rate of gross motor dysfunction.2
Mechanism of Action
Vasodilatory Effects of Magnesium
- Magnesium is a calcium antagonist and a potent vasodilator of uterine and mesenteric arteries, and aorta. It has minimal vasodilatory effects on cerebral vessels.3
- In vascular smooth muscles, magnesium competes with calcium for binding sites, such as the voltage-operated calcium channels, decreasing intracellular calcium levels and, thereby, causing vasodilation.3
- In the endothelium, magnesium increases the production of prostaglandin I2, resulting in decreased platelet aggregation. Magnesium also increases nitric oxide production, causing vasodilation.3
Effects on Cerebral Edema
- Magnesium decreases blood-brain barrier disruption and limits cerebral edema formation via paracellular transport. As a calcium antagonist, magnesium decreases endothelial cell contraction and opening of tight junctions. The decreased tight junction permeability limits the paracellular transport of vascular contents, ions, and proteins that cause vasogenic edema.3
Anticonvulsant Effects
- The exact mechanism by which magnesium functions as an anticonvulsant is unclear.
- Magnesium increases seizure threshold by acting as an N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonist and limiting the effects of glutamate, thereby preventing massive neuronal depolarization.3
Neuroprotective Effects
The mechanism for the neuroprotective effects of magnesium in preterm infants is not well understood. Possible mechanisms include4
- stabilization of cerebral vasculature by stabilizing the blood pressure and normalizing cerebral blood flow;
- stabilization of neuronal membranes and blockade of excitatory neurotransmitters, such as glutamate;
- antioxidants effects; and
- anti-inflammatory effects.
Administration
Magnesium sulfate is the formulation commonly given IV.
Seizure Prophylaxis
- Therapy with magnesium should be started at induction or at the beginning of labor.
- Intravascular regimen
- 4-6 g loading dose over 30 minutes
- Infusion of 1-2 g/hour until 24-48 hours postpartum
- Intramuscular regimen
- 10 g loading dose (5 g per buttock)
- Injection of 5 g every 4 hours until at least 24 hours postpartum
- If there is a seizure with either regimen, a 2-4 g bolus can be given over a period of at least 5 minutes.
- For patients undergoing cesarean delivery, magnesium should be started 2 hours before the procedure, continued intraoperatively and for 24 hours postpartum.
Fetal Neuroprotection
- Magnesium should be given as close as possible to 4 hours before delivery. If delivery is anticipated sooner than 4 hours, magnesium should still be given.
- Typically, a 4 g loading dose is administered over 30 minutes, followed by an infusion of 1 g/hour until the birth of the baby. The infusion should be stopped after 24 hours if there is no delivery.
Adjunct Agent with Induction of General Anesthesia
- In women with preeclampsia, administration of a magnesium bolus after induction can reduce the hypertensive response to intubation.5 The suggested dose is 30 mg/kg if on magnesium already and 45 mg/kg if magnesium naïve.
Safety & Drug Toxicity6
- Magnesium increases the risk of postpartum hemorrhage.
- After administration, about 40% of plasma magnesium is protein-bound. Magnesium is eliminated by renal excretion.
- The normal range of serum magnesium is 1.8 to 2.4 mg/dL (1.2-2 mEq/L), and the therapeutic range of serum magnesium is 5 to 9 mg/dL (4-8 mEq/L) (Table 1). Side effects in the therapeutic range include nausea/vomiting and headache. Approximately 25% of patients experience side effects.
- Patients on magnesium infusions should be frequently monitored for signs of hypermagnesemia.
- The signs and symptoms of hypermagnesemia are listed in Table 1. Please note the units of measurement used.
- EKG changes (prolonged PR, widened QRS): 6-12 mg/dL (5-10 mEq/L)
- Loss of deep tendon reflexes (patellar commonly checked): 12 mg/dL (10 mEq/L)
- Respiratory arrest, SA/AV node block: 15 to 20 mg/dL (15 mEq/L)
- Cardiac arrest: ≥ 24 mg/dL (20 mEq/L)
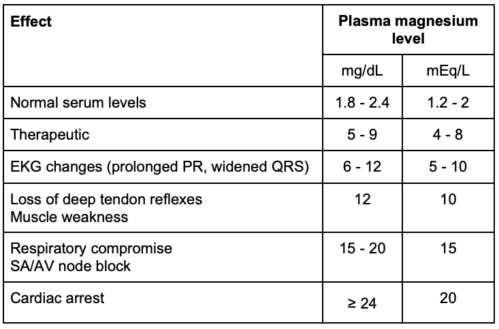
Table 1. Dose effect at different magnesium levels
- Treatment of hypermagnesemia
- The magnesium infusion should be discontinued.
- Calcium gluconate 1g IV should be administered over ten minutes.
- Symptomatic management should be continued.
- Contraindications
- Magnesium should be used with caution in patients with myasthenia gravis or renal impairment.
Drug Interactions
- Magnesium potentiates the effect of nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agents and prolongs the effects of rocuronium, cisatracurium, and vecuronium. If muscle relaxation is needed intraoperatively, small doses of a nondepolarizing neuromuscular blocking agent can be used with titration to a twitch monitor.
- Magnesium does not potentiate succinylcholine, so it can be safely used for rapid sequence intubation. Fasciculations may be decreased or absent with succinylcholine administration.
- Other drug interactions with magnesium are listed in Table 2.
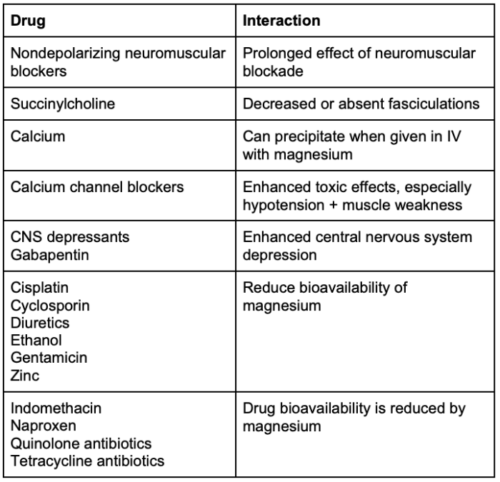
Table 2. Drug interactions with magnesium
Other Uses
Pain Management
- Neuraxial
- When given via epidural or spinal routes for cesarean delivery, magnesium can increase the time to first analgesic request.
- There are limited data on the risk of neurologic complications and the dose-response curve.
- IV
- Some studies have shown mild decreases in pain scores after anesthesia when IV magnesium is given for nonobstetric surgery.
- Magnesium’s role in cesarean delivery is unclear.
Preterm Labor Tocolysis
- Magnesium is a tocolytic.
- A meta-analysis demonstrated that magnesium was ineffective at delaying or preventing preterm birth. Additionally, compared to other tocolytics, when magnesium was used for this indication, it was associated with increased fetal, neonatal, and infant mortality.7
Tocolysis for Fetal Surgery
- Magnesium is commonly used as a tocolytic during open or fetoscopic mid-gestation fetal surgeries, such as fetal myelomeningocele repairs.8
References
- Doyle LW, Crowther CA, Middleton P, et al. Magnesium sulphate for women at risk of preterm birth for neuroprotection of the fetus. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2009;(1):CD004661. PubMed
- Duley L, Gülmezoglu AM, Henderson-Smart DJ, et al. Magnesium sulphate and other anticonvulsants for women with pre-eclampsia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2010;2010(11):CD000025. PubMed
- Euser AG, Cipolla MJ. Magnesium sulfate for the treatment of eclampsia: a brief review. Stroke. 2009;40(4):1169-75. PubMed
- Simhan HN, Himes KP. Neuroprotective effects of in utero exposure to magnesium sulfate. In: Post T (ed). UpToDate. 2023. Link
- James MF, Dyer RA. Prevention of peri-induction hypertension in pre-eclamptic patients. Anesth Analg. 2015;121(6):1678-79. PubMed
- Lu JF, Nightingale CH. Magnesium sulfate in eclampsia and pre-eclampsia: pharmacokinetic principles. Clin Pharmacokinet. 2000;38(4):305-14. PubMed
- Crowther CA, Brown J, McKinlay CJ, et al. Magnesium sulphate for preventing preterm birth in threatened preterm labour. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2014;(8):CD001060. PubMed
- Hoagland MA, Chatterjee D. Anesthesia for fetal surgery. Paediatr Anaesth. 2017; 27(4): 346-57. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.