Copy link
Diuretics
Last updated: 05/02/2024
Key Points
- Diuretics are a diverse class of medications used to manage fluid and electrolyte imbalances by increasing urine output.
- Common classes of diuretics used include thiazide, loop, potassium-sparing, and osmotic diuretics, each with distinct mechanisms of action and clinical indications.
- Many of the clinical indications and side effects of diuretics are related to their effects on electrolyte and fluid balances.
Introduction
- Diuretics are a group of drugs used to increase urine output and are often used to remove excess fluid or electrolytes from the body. They are categorized into several classes based on their mechanisms of action and clinical applications. Commonly used classes of diuretics include thiazide diuretics, loop diuretics, potassium-sparing diuretics, and osmotic diuretics.
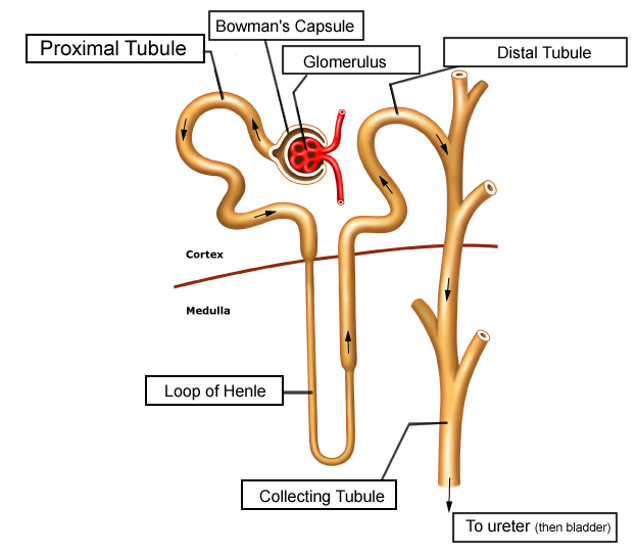
- Diuretics exert their actions by altering the function of various regions of the nephron, as shown in Figure 1.
Thiazide Diuretics
Introduction
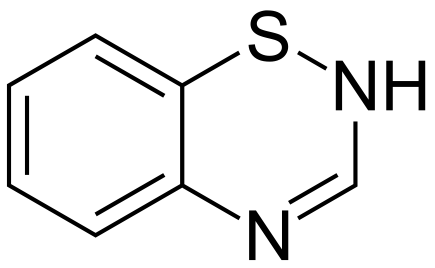
- Thiazide diuretics are a class of diuretics based on the chemical structure of benzothiadiazine, a bicyclic organic molecule containing sulfur, as seen in Figure 2.
- Common thiazide diuretics include hydrochlorothiazide, chlorthalidone, metolazone, and chlorothiazide.
Mechanism of Action1
- Thiazide diuretics work primarily by inhibiting the sodium-chloride cotransporter of the distal convoluted tubule of the nephron in the kidney. The blocked reabsorption of sodium and chloride leads to increased excretion in the urine.
- Thiazide diuretics increase calcium reabsorption through the increased activity of the sodium-calcium exchanger of the distal convoluted tubule.
- Increased sodium flow to the collecting tubule increases the aldosterone-mediated actions of the collecting tubule’s sodium-potassium pump, increasing the excretion of potassium and hydrogen ions into the urine.
Clinical Indications
- Hypertension: Patients may require evaluation of electrolytes.2
- Edema or fluid overload associated with congestive heart failure:3
- Thiazide diuretics can be combined with loop diuretics to treat diuretic-resistant edema in nephrotic syndrome.4
- Prevention of calcium kidney stones3
- Arginine vasopressin resistance (nephrogenic diabetes insipidus)3
Side Effects and Contraindications
- The side effects of thiazide diuretics are secondary to their effects on various electrolyte balances (Table 1).2,3

Table 1. Electrolyte disturbances of thiazide diuretics
- Metabolic disturbances (e.g., hyperglycemia, hyperlipidemia)2,3
- Caution for exacerbated hyperglycemia in patients with prediabetes or diabetes mellitus
- Caution for exacerbated hyperlipidemia in patients with hypercholesterolemia or metabolic syndrome
- Thiazide diuretics can induce hypotension, particularly when combined with other antihypertensive medications acting on the renin–angiotensin system (angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitors/angiotensinogen receptor blockers).3
- Negative effects on male sexual function (e.g., decreased libido, erectile dysfunction, and difficult ejaculation) have been reported.3
- Thiazide diuretics should be avoided in patients with known sulfonamide hypersensitivity due to the risk of allergic reactions.3
- Thiazide diuretics should be avoided in patients with anuria or severe renal impairment.2,3
Loop Diuretics
Introduction
- Loop diuretics are the most potent of diuretics.
- Common loop diuretics include furosemide, torsemide, bumetanide, and ethacrynic acid.
- Most loop diuretics are sulfonamides (furosemide, torsemide, bumetanide).
Mechanism of Action1
- Loop diuretics inhibit the sodium-potassium-chloride cotransporter of the medullary thick ascending loop of Henle, leading to increased excretion of these ions in the urine.
- Decreased potassium recycling disrupts the positive luminal voltage gradient, inhibiting the reabsorption of calcium and magnesium.
- Loop diuretics increase the release of prostaglandins, resulting in vasodilation and increased renal blood flow.
Clinical Indications
- Edema or fluid overload is associated with conditions such as congestive heart failure, liver cirrhosis, or nephrotic syndrome.3
- Hypertension: Add-on therapy should be considered in patients being treated with other antihypertensives. An antihypertensive treatment should be considered for patients with impaired renal function (glomerular filtration rate <30mL/min).3
- Renal failure: Loop diuretics are the preferred diuretic in patients with impaired renal function (glomerular filtration rate <30mL/min).3
- Cerebral edema or increased intracranial pressure: An add-on therapy to an osmotic diuretic, such as mannitol, should be considered.5
- Hypercalcemia2,3
- Severe hyperkalemia3
- Forced diuresis of toxic substances (e.g., toxins, drugs, myoglobin in rhabdomyolysis)6
Side Effects and Contraindications
- Electrolyte disturbances (e.g., hyponatremia, hypokalemia, hypomagnesemia, hyperuricemia, metabolic alkalosis)2,3
- Hyperuricemia can present as drug-induced gout. Loop diuretics are contraindicated in patients with gout.3
- Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia can present as life-threatening cardiac arrhythmias.
- Hypotension: Caution should be exercised with the use of other diuretics.3
- Fluid imbalance and dehydration: Contraindicated in severe hypovolemia2,3
- Ototoxicity is a rare complication of loop diuretic use. It can present as transient or permanent hearing damage. Ethacrynic acid may be more ototoxic.7
- Sulfonamide-based loop diuretics should be avoided in patients with known sulfonamide hypersensitivity. The use of ethacrynic acid should be considered.3
- Avoid in patients with anuria2,3
Potassium-Sparing Diuretics
Introduction
- Potassium-sparing diuretics cause diuresis without the excretion of potassium.
- There are two main classes of potassium-sparing diuretics: aldosterone antagonists and epithelial sodium channel blockers.
- Common aldosterone antagonists include spironolactone and eplerenone.
- Common epithelial sodium channel blockers include amiloride and triamterene.
Mechanism of Action1
- Aldosterone antagonists
- Aldosterone is a hormone that promotes sodium reabsorption in exchange for potassium secretion in the distal nephron.
- Aldosterone antagonists competitively bind to and inhibit the aldosterone receptors in the distal tubule and collecting duct, thus inhibiting the effects of aldosterone. This leads to increased excretion of sodium and retention of potassium.
- Inhibition of H+/ATPases of the distal tubule and collecting duct causes decreased hydrogen ion excretion.
- Epithelial sodium channel blockers
- Epithelial sodium channels facilitate sodium reabsorption in exchange for potassium secretion in the distal tubule and collecting duct.
- Epithelial sodium channel blockers inhibit these channels, increasing sodium excretion and potassium retention.
Clinical Indications
- Hypertension, particularly when comorbid hypokalemia is present, and potassium-sparing diuretics are considered as additional therapy for resistant hypertension.2,3
- Primary hyperaldosteronism3
- Heart failure3
- Use of spironolactone in hyperandrogenic states (e.g., female acne vulgaris, female hirsutism, or female-patterned baldness)8
Side Effects and Contraindications
- Electrolyte disturbances (e.g., hyperkalemia, hyponatremia, metabolic acidosis)2,3
- Hyperkalemia, if severe, can lead to cardiac arrhythmias.
- Gastrointestinal disturbances (e.g., nausea, vomiting, diarrhea)3
- Endocrine disturbances.
- In men, antiandrogenic effects can lead to gynecomastia, decreased libido, and erectile dysfunction.2,3
- Avoid in patients with anuria or severe renal impairment2,3
Osmotic Diuretics (Mannitol)
Introduction
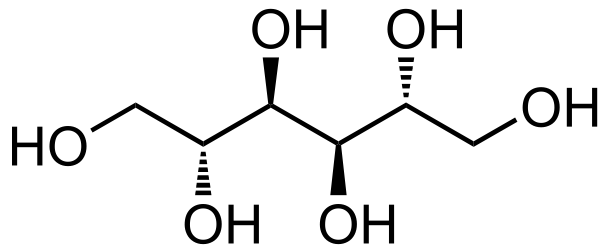
- Mannitol, a naturally occurring sugar alcohol, is the most commonly used osmotic diuretic (Figure 3). It is available as a 10% or 20% solution in a 500 mL bag of sterile water containing 50g or 100g of mannitol, respectively. Mannitol can crystallize if stored at room temperature but can be made soluble again by warming the solution.6
Mechanism of Action6
- Osmotic diuretics are freely filtered across the glomerulus and are unable to be reabsorbed by the renal tubules. The increased osmolarity of the glomerular filtrate prevents reabsorption of water and electrolytes leading to increased urine production.
- Additionally, osmotic diuretics increase serum osmolarity, promoting fluid shift into the intravascular space and decreasing extravascular pressures (e.g., intracranial, intraocular).
Clinical Indications
- Elevated intracranial pressure (e.g., cerebral edema)3,6
- Elevated intraocular pressure (e.g., acute glaucoma, traumatic hyphema)6
- Mannitol provides renal protection in cases of decreased renal blood flow (e.g., kidney transplantation, acute renal injury in oliguria). It also improves renal cortical flow and is preferred to optimize intravascular volume status.6
- Forced diuresis of toxic substances (e.g., toxins, drugs, myoglobin in rhabdomyolysis)6
Side Effects and Contraindications
- Fluid imbalance and dehydration: Mannitol is contraindicated in severe hypovolemia.3,6
- Initial intravascular volume shift can cause volumetric strain, potentially worsening heart failure and pulmonary congestion.3,6
- Electrolyte abnormalities, most commonly hypernatremia6
- Repeated administration can result in high serum osmolarity and neurological complications.
References
- Rose BD. Diuretics. Kidney Int. 1991;39(2):336-52. PubMed
- Kiefer J, Mythen M, Roizen MF, Fleisher LA. Anesthetic Implications of Concurrent Diseases. In: Gropper MA, et al (eds). Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2019: 999-1064.
- Roush GC, Kaur R, Ernst ME. Diuretics: a review and update. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol Ther. 2014;19(1):5-13. PubMed
- Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO) Glomerular Diseases Work Group. KDIGO 2021 Clinical Practice Guideline for the Management of Glomerular Diseases. Kidney Int. 2021;100(4S):S1-S276. PubMed
- Lemkuil BP, Drummond JC, Patel PM, Lam A. Anesthesia for Neurologic Surgery and Neurointerventions. In: Gropper MA, et al (eds). Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Elsevier; 2019: 1868-1910.
- Shawkat H, Westwood MM, Mortimer A. Mannitol: a review of its clinical uses. Contin Educ Anaesth Crit Care Pain. 2012;12(2):82-5. Link
- Ding D, Liu H, Qi W, et al. Ototoxic effects and mechanisms of loop diuretics. J Otol. 2016;11(4):145-56. PubMed
- Searle TN, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR. Spironolactone in dermatology: uses in acne and beyond. Clin Exp Dermatol. 2020;45(8):986-93. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.