Copy link
Chronic Liver Disease and Cirrhosis
Last updated: 12/13/2023
Key Points
- Chronic liver disease (CLD) manifests as a deterioration in liver function over a period of greater than 6 months.
- Cirrhosis occurs towards the end of the CLD process when the tissue scarring from inflammation and fibrosis culminates in disruptive remodeling of the liver. This results in a further deterioration of hepatic function.
- Most patients are unaware that they have CLD or cirrhosis.
- Treatments are aimed at the avoidance of further disease progression and the prevention of hepatic decompensation.
- In patients with CLD, multiple organ systems are usually involved.
Introduction
- The etiology of CLD is varied. The most common causes are chronic viral hepatitis from hepatitis B virus (HBV) and/or hepatitis C virus (HCV), and fatty liver disease, which includes both nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and alcoholic liver disease. Other causes include diseases with a genetic or autoimmune basis (Table 1).
- CLD and hepatic cirrhosis are a leading cause of mortality and morbidity across the world. In 2020, CLD/cirrhosis was the 12th leading cause of death across the United States, with a rate of 15.7 per 100,000 population.1
- Across the world, an estimated 1.5 billion people have some degree of CLD.2,3
- Chronic viral infection (hepatitis B, C, and D) remains the most common cause of CLD in Asia and Sub-Saharan Africa.
- Obesity and excess alcohol consumption are both primary causes and cofactors leading to an increase in the prevalence of nonviral CLD worldwide.
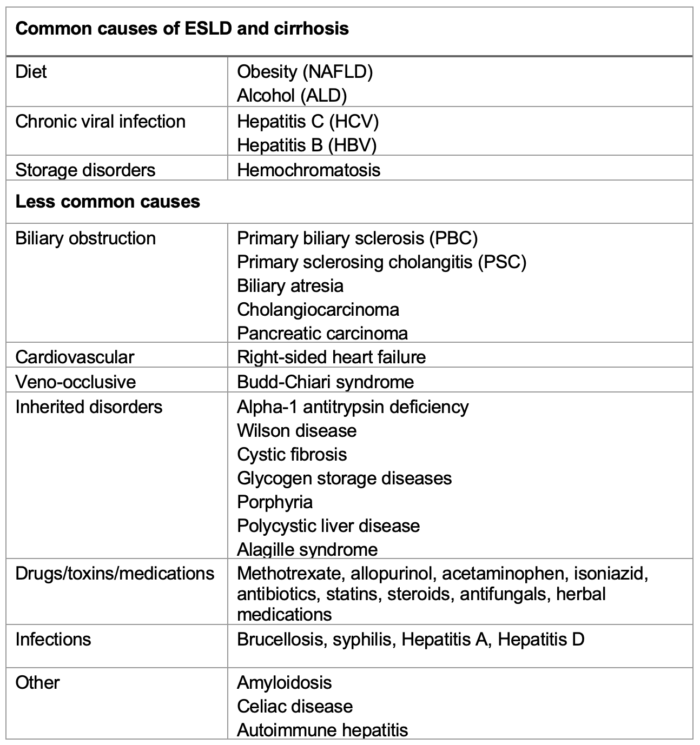
Table 1. Causes of ESLD and cirrhosis.
Abbreviations: NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; ALD, alcoholic liver disease
Pathophysiology
- Hepatocellular damage activates the previously dormant hepatic stellate cells (HSC) which undergo differentiation into myofibroblasts. The myofibroblasts produce an extracellular matrix which acts as a temporary scar to protect the damaged tissue.
- The activated HSC also stimulate angiogenesis and the regeneration of hepatocytes.4
- Recurring episodes of hepatocellular damage lead to an increased and sustained level of HSC activity.
- As CLD progresses, a chronic inflammatory process develops, which cycles through phases of tissue regeneration, angiogenesis, and fibrosis. This scarring ultimately leads to the distortion of the normal hepatic architecture and is responsible for the nodular appearance of the cirrhotic liver.
- Normal blood flow through the liver segments gets disrupted. Intrahepatically, sinusoidal blood flow relies on the balance between vasoconstrictors (e.g., endothelin, thromboxane, norepinephrine, angiotensin-II) and vasodilators (e.g., nitric oxide) produced by the sinusoidal endothelial cells. Hepatocellular damage and subsequent fibrosis causes intrahepatic vasoconstriction and an increase in the resistance to blood flow within the portal system, which leads to the development of portal hypertension (PH).
- Extrahepatically, there is an increase in the production of nitric oxide, resulting in both systemic and splanchnic vasodilatation. The resulting hypotension then activates the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone (RAA) system, thereby promoting fluid retention and the development of a hyperdynamic systemic circulation.
- The PH (with the resulting hyperdynamic circulation) is responsible for most of the complications of cirrhosis.
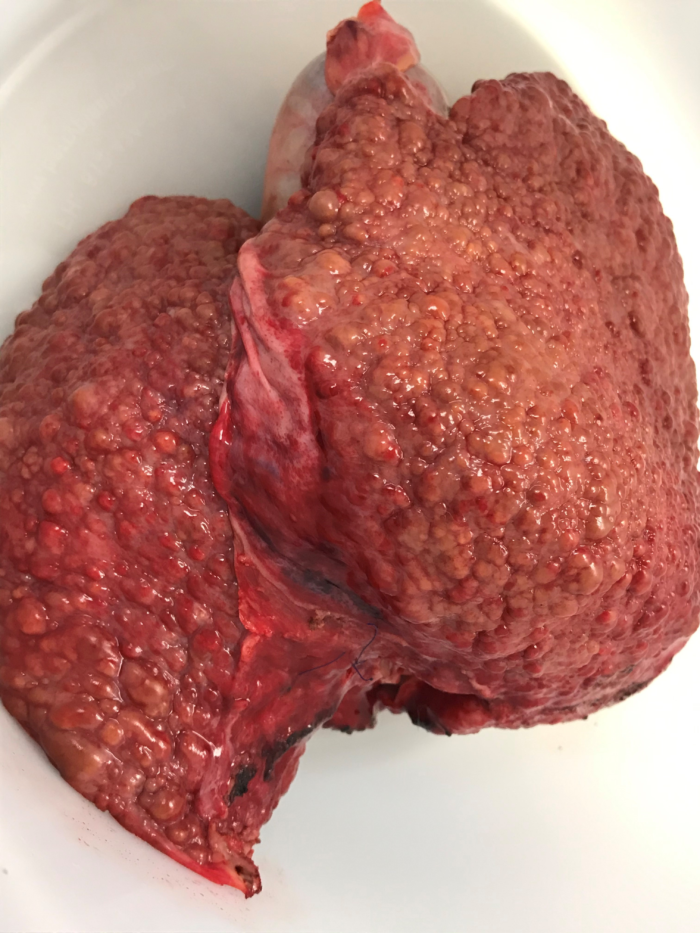
Figure 1. Cirrhotic liver after hepatectomy during orthotopic liver transplant. Image courtesy: Jennifer Cutler, MD
Presentation
- Most patients with cirrhosis will not have symptoms of the underlying disease.
- As the disease progresses, common signs and symptoms include weakness, fatigue, nausea, weight loss, jaundice, itching, fluid retention, and abdominal pain.
- Diagnosis can be accomplished by imaging the liver (ultrasound, liver elastography, computerized tomography or magnetic resonance imaging) and looking for laboratory evidence of decreased liver function from blood serum samples (e.g., aspartate aminotransferase, alanine aminotransferase, bilirubin, international ionized ratio, platelet count, etc.).
- A histological diagnosis made from a liver biopsy is the gold standard for diagnosing CLD. However, because it is an invasive test, many practitioners choose to follow the progression of the liver disease with noninvasive investigations.
- CLD or cirrhosis without complications is said to be “compensated” liver disease. Once symptoms appear, then the disease is usually described as “decompensated.” Events associated with the progression to decompensation include sepsis, upper gastrointestinal bleeding, the development of ascites, and encephalopathy. Undergoing surgery can cause decompensation in a previously stable patient.
- Prevention of decompensation is key. Lifestyle changes (refraining from alcohol consumption, losing weight, improving nutrition, stopping smoking) are beneficial. Vaccination against HBV, HCV, and influenza should be undertaken. Treatment for the underlying cause of liver disease can help reduce the rate of disease progression. Antiviral therapy should be implemented for those with HBV/HCV.
Portal Hypertension and Associated Complications
- PH develops as the blood flow through the liver meets increasing resistance in the hepatic sinusoids. The measurement of the hepatic venous pressure gradient (HVPG) allows a rigorous assessment of PH and can be used to predict disease progression as well as monitor the response to different medication regimens.
- An HVPG greater than 5 mmHg is consistent with a diagnosis of portal hypertension, while an HVPG greater than 10 mmHg represents clinically significant PH, which increases the likelihood of developing esophageal varices, as alternative ways are found for the return of blood to the IVC.5
- Once a patient develops significant PH, they are at risk of further developing several complications (Figure 2).
- Ascites – retained fluid (from the RAAS activation) is squeezed out into the abdominal cavity from the splanchnic bed due to the increased intrahepatic pressure and low oncotic pressure due to hypoalbuminemia.
- Hepatorenal syndrome (HRS) – a worsening renal function brought about by renal artery vasoconstriction from chronic stimulation by RAAS alongside the raised intra-abdominal pressure from abdominal ascites.
- Hepatic encephalopathy (HE) – with the portal flow diverted away from the liver through portosystemic shunts or passing through metabolically inactive areas of the remaining liver tissue, there is loss of the first pass metabolism and the blood is not cleared of toxins (e.g., ammonia, short-chain fatty acids, mercaptans, false neurotransmitters and GABA). These toxins can cross the blood-brain barrier to cause a spectrum of reversible neuropsychiatric abnormalities.
- Spontaneous bacterial peritonitis – worsening liver function is associated with increased mortality from infections that often develop secondary to translocation of gut bacteria from the GI tract. The translocation is multifactorial as it has been shown to be due to bacterial overgrowth, decreased bowel motility, and increased gut wall permeability.
- Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) – the development of HCC is linked to the background of chronic inflammation and to immunomodulation triggered by senescent hepatocytes and HSCs.6 Approximately 80% of patients with HCC have underlying cirrhosis.
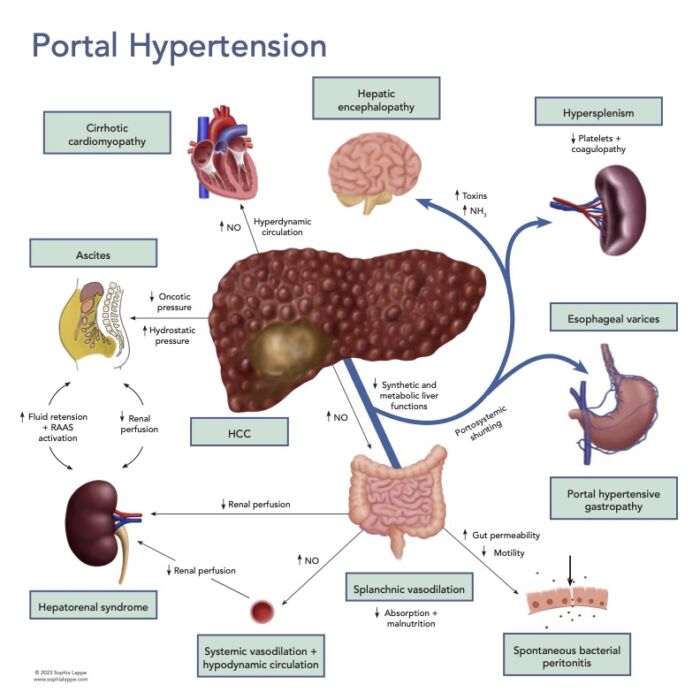
Figure 2. Portal hypertension and associated complications
Abbreviations: NO = nitric oxide, HCC = hepatocellular carcinoma, NH3 = ammonia, RAAS = Renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system.
Management of CLD
- The aim of treatment in CLD is to prevent further deterioration of the disease.
- Variceal disease and ascites can be managed using vasopressors (e.g., terlipressin), β-blockers, (e.g., propranolol, nadalol), and diuretics (furosemide and spironolactone). Endoscopic banding/sclerotherapy of varices is undertaken when necessary and transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts can be placed to reduce the portal pressure. Albumin infusions and therapeutic paracentesis are also common therapies.
- Lactulose and rifaximin are useful treatments for HE. Both aim to reduce the ammonia concentration in the blood.
- HRS is a consequence of the under-perfusion of the kidneys secondary to splanchnic vasodilation and the raised intra-abdominal pressure brought about by ascites. Vasopressors (e.g., terlipressin) and intravascular fluid resuscitation are the mainstays of management.
- Preoperative scoring systems are used to predict the risk of nonoperative morbidity and mortality. The most widely used are the Model-for End-Stage Liver Disease score (including multiple variations) and the Child-Turcotte-Pugh score.
Anesthetic Considerations7
- Patients with CLD have an increased risk of morbidity and mortality during surgery, and even a well-performed surgical and anesthetic procedure can provoke decompensation.
- Preoperative management should focus on optimizing liver function and treating any associated issues¬ – coagulopathy, ascites, encephalopathy, PH, and renal failure.
- The choice of anesthetic technique depends on the urgency of the case, nature of the surgery, and the condition of the patient. There is no single best option.
- Monitoring during the case uses more invasive modalities than with non-CLD patients. Arterial lines are regularly placed, and the use of transesophageal echocardiography has become commonplace.
- Regional and neuraxial techniques are popular, but existing or predicted worsening of coagulopathy can make the choice controversial.
- The preservation of hepatic blood flow is an important factor. Both neuraxial and general anesthetic techniques, using intravenous anesthetic drugs or volatile agents, can cause significant falls in blood pressure and hepatic blood flow.
- Drug handling by the diseased liver can be unpredictable but, in general, alterations to metabolic pathways, protein binding, and volume of distribution require both dosage and timing modifications.
- Multimodal analgesia including regional anesthesia is a proven option. Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs are often disregarded due to the risk of renal toxicity and increased bleeding. Opioids and sedatives should be used judiciously, especially in patients with hepatic encephalopathy.
- Viscoelastic testing is often used to guide the perioperative management of coagulopathy. Platelet counts and fibrinogen levels are often low, and laboratory measurements of clotting indices are usually abnormal.
References
- American Liver Foundation. How many people have liver disease? Accessed Apr 2023. Link
- Cheemerla S, Balakrishnan M. Global epidemiology of chronic liver disease. Clin Liver Dis (Hoboken). 2021;17(5):365-70. PubMed
- Moon AM, Singal AG, Tapper EB. Contemporary epidemiology of chronic liver disease and cirrhosis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2020;18: 2650‐66. PubMed
- Yin C, Evason KJ, Asahina K, et al. Hepatic stellate cells in liver development, regeneration, and cancer. J Clin Invest. 2013;123(5):1902-10. PubMed
- Suk KT. Hepatic venous pressure gradient: clinical use in chronic liver disease. Clin Mol Hepatol. 2014;20(1):6-14. PubMed
- Liu P, Tang Q, Chen M, et al. Hepatocellular senescence: Immunosurveillance and future senescence-induced therapy in hepatocellular carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020; 10:589908. PubMed
- Steadman RH. Anesthesia for the patient with liver disease. Post TW, ed. UpToDate. Waltham, MA: UpToDate. 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.