Copy link
Cancer Pain: WHO Analgesic Ladder
Last updated: 03/14/2023
Key Points
- Cancer-related pain is experienced by most patients undergoing anticancer treatment and those with advanced disease.1
- The World Health Organization (WHO) guidelines for the pharmacological and radiotherapeutic management of cancer pain in adults and adolescents provide general recommendations for the approach to cancer-related pain.
- The WHO analgesic ladder is a simple three-step approach to cancer-related pain which has been shown to be effective in helping 70-80% of patients find pain relief.2
WHO Cancer Pain Guidelines
Pain is experienced by about 55% of patients undergoing anticancer treatment and up to 66% of patients with advanced or terminal disease.1 The WHO analgesic ladder, originally introduced in 1986, provides a standardized approach to managing cancer-related pain. The most recent guidelines released in 2018 are applicable to individuals 10 years and older and include both pharmacologic as well as radiotherapeutic pain management recommendations.
Guiding principles in the most recent recommendations include:
- optimizing pain management to allow for an acceptable quality of life;
- recognizing that individuals may experience and describe their pain differently;
- integrating psychosocial and spiritual care into pain management plans as needed;
- combining pain management into a patient’s overall cancer care; and
- administrating analgesics, which should be:
- By mouth: Oral agents should be preferred over other routes of administration.
- By the clock: Dosing should be scheduled at fixed intervals of time rather than on-demand administration.
- For the individual: The etiology of each patient’s pain should be assessed and treated accordingly (e.g., neuropathic vs. visceral vs. somatic pain).
- With attention to detail: The first and last daily doses should align with the patient’s normal sleep schedule. The recommendation is to provide specific administration instructions, including possible adverse effects from medications to patients and their caregivers.
WHO Three-Step Analgesic Ladder
The general recommendation in the initiation of cancer pain management is to include nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), acetaminophen, and opioids either alone or in combination, depending on the current pain severity, to achieve rapid and safe pain control.1 In addition, adjuvants including steroids, antidepressants, anticonvulsants, and bisphosphonates can be utilized depending on the patient’s unique situation.1 The three-step analgesic ladder below has been a consistent aspect of the WHO cancer pain guidelines, demonstrating how to develop an escalating pain management regimen. It has been shown that with the three-step analgesic approach, 70-80% of patients can find pain relief.2
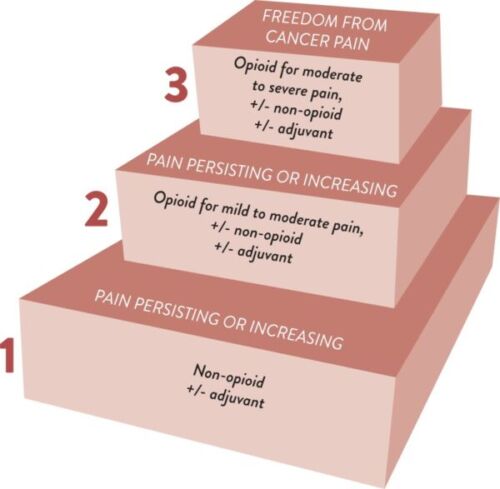
Figure 1. The WHO three-step analgesic ladder. Source: WHO guidelines for the pharmacological and radiotherapeutic management of cancer pain in adults and adolescents. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. PubMed. CC-BY-NC-SA-3.0 IGO.
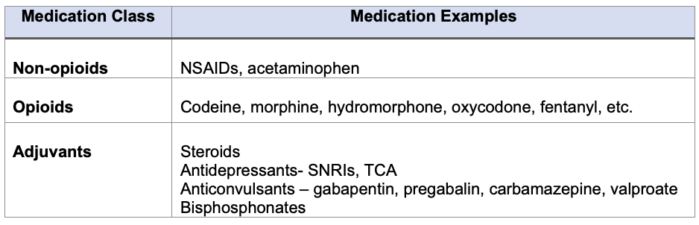
Table 1. Classes of medications included in the WHO three-step analgesic ladder. (NSAIDS = non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, SNRI = serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, TCA = tricyclic antidepressants)
Although not an official aspect of the WHO three-step analgesic ladder, some authors have proposed the addition of a fourth level which would include interventions such as:3
- Epidural analgesia
- Intrathecal medication administration
- Neurosurgical procedures
- Neuromodulation
- Nerve blocks
- Ablative procedures
These procedures, although effective for patients, are currently not addressed in the current WHO recommendations for cancer pain.1
Pharmacologic and Radiotherapeutic Management Recommendations
Opioid Recommendations1
- Any opiate may be considered as long as it is effective and safe for the patient.
- Either an immediate-release or slow-release opiate can be utilized.
- Breakthrough pain should be treated with a rescue immediate-release opioid.
- No recommendation was made for or against rotating between opioid medications.
- Oral route of administration should be preferred.
Adjuvant Recommendations1
- Steroids should be given for pain control when indicated but used for as short a time as possible.
- No formal recommendation was made for or against using tricyclic antidepressants, gabapentin, pregabalin, carbamazepine, valproate, and SNRIs to treat cancer-related neuropathic pain. There is a comment that these medications can be utilized for patients who are not achieving adequate analgesia.
Bone Pain Recommendations1
- In patients with bony metastases and bone pain, bisphosphonates should be utilized.
- No recommendation was made for or against monoclonal antibodies for bone cancer-related pain.
- Radiotherapy should be utilized for cancer-related bone pain when available and indicated.
References
- World Health Organization. WHO guidelines for the pharmacological and radiotherapeutic management of cancer pain in adults and adolescents. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2018. Accessed November 11th, 2022. Link
- Anekar AA, Cascella M. WHO Analgesic Ladder. StatPearls. Published January 2022. Updated May 15, 2022. Accessed November 11, 2022. Link
- Ashburn, MA, Lipman AG. Management of pain in the cancer patient. Anesth Analg. 1993; 76 (2): 402-16. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.