Copy link
Pyloric Stenosis
Last updated: 06/20/2024
Key Points
- Pyloric stenosis is an abnormal thickening of the pylorus muscle in the stomach that causes gastric outlet obstruction.
- Persistent vomiting results in dehydration and hypokalemic, hypochloremic metabolic alkalosis that must be corrected before surgery.
- Gastric decompression prior to induction, followed by rapid sequence induction and intubation for general endotracheal anesthesia, is typically recommended.
Introduction and Epidemiology
- Pyloric stenosis is an abnormal thickening of the pylorus muscle in the stomach, which leads to gastric outlet obstruction (Figure 1).1-4
- Incidence is approximately 1-5 /1000 live births.1
- Pyloric stenosis is 4-5 times more common in males than females.1,2
- There is a decreased incidence with increasing birth order.1,2
- In the United States, pyloric stenosis is more common in Caucasians compared to Asians or African Americans.1,3,4
- While the exact etiology is unclear, pyloric stenosis arises from a polygenic inheritance with modification from several environmental factors, including macrolide antibiotics, hypergastrinemia, bottle feeding, preterm birth, cesarean section delivery, maternal smoking during pregnancy, and younger maternal age.1-4
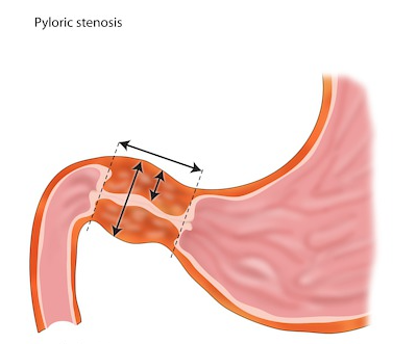
Figure 1. Thickened pylorus with narrowed gastric outlet. Case courtesy of Frank Gaillard, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 8145.
Pathophysiology
- The primary pathophysiology is gastric outlet obstruction from a hypertrophied pylorus.1-4
- Persistent vomiting results in the loss of gastric juices (mainly hydrogen and chloride ions and, to a lesser degree, sodium and potassium ions), resulting in hypochloremic hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis.1-4
- Initially, alkaline urine is produced to compensate for the metabolic alkalosis. However, with worsening dehydration, the kidneys try to preserve plasma volume and secrete hydrogen ions in exchange for sodium and water, resulting in paradoxical acidic urine.2
- Cerebrospinal spinal fluid (CSF) alkalosis causes respiratory depression and apnea. Even after the correction of metabolic alkalosis, the calibration of CSF pH with plasma pH takes several hours, putting these patients at risk for postoperative apnea.2
Presentation and Diagnosis
Clinical Presentation
- Symptoms usually present around 3-5 weeks of age.1-4
- Pyloric stenosis results in projectile non-bilious post-prandial vomiting. This results in dehydration and hypochloremic hypokalemic acidosis. Persistent vomiting can result in weight loss or failure to gain weight.1-4
Diagnosis
- A detailed history should be obtained to evaluate for other conditions such as feeding intolerance, gastroesophageal reflux, food allergies, infection, and structural or systemic disease.1-4
- The classic diagnostic finding is the palpation of a firm olive-shaped mass at the lateral edge of the rectus abdominis muscle in the right upper abdominal quadrant.1-4
- Diagnosis is typically confirmed on imaging.5
- Ultrasound is the preferred imaging modality. A pyloric wall thicker than 3mm (Figure 2) and a pyloric channel longer than 18 mm (Figure 3) is diagnostic.
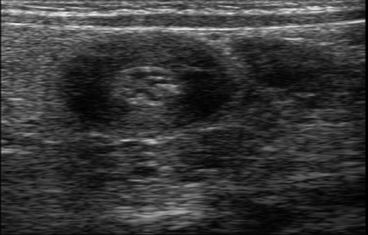
Figure 2. Thickened pyloric wall. Case courtesy of Hidayatullah Hamidi, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 51340.
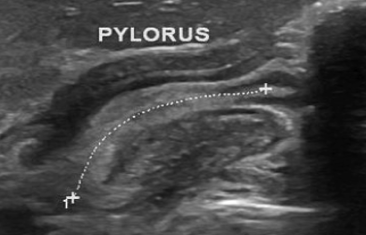
Figure 3. Lengthened pyloric canal. Case courtesy of Maulik S Patel, Radiopaedia.org, rID: 55414.
-
- Barium upper gastrointestinal series are not preferred due to the risks of ionizing radiation. A narrowing of the pyloric canal “string” sign or barium at the pyloric canal “beak” sign can be visualized.
Treatment
Initial Management
- Pyloric stenosis is a medical, not a surgical emergency.1-3
- The correction of dehydration and metabolic alkalosis is indicated prior to surgical repair.1-4
- The patient is kept nil per os, and isotonic crystalloids should be administered for volume resuscitation. Adequate resuscitation is typically completed in 12-48 hours. Maintenance fluids with dextrose at 1.5-2 times maintenance should be continued. Renal function should be assessed before adding potassium to maintenance fluids.1-4
- The correction of electrolyte abnormalities should target serum chloride of more than 100 mEq/L and serum bicarbonate of less than 30 mEq/L. The patient voiding is another sign of adequate resuscitation.1-3
Surgical Techniques
- Pyloromyotomy involves an incision on the pylorus and blunt dissection to the submucosa.2
- Open approach via a right upper quadrant transverse or umbilical incision (Figure 4).2-3
- A laparoscopic approach is commonly used (Figure 5).2-3
- A study comparing the two approaches found similar operating time, time to full feeding and length of hospital stay but fewer episodes of vomiting and decreased use of analgesics in the laparoscopic group.3
- Another study showed a faster return to enteral feeding and shorter hospital stays but higher rates of incomplete pyloromyotomy in the laparoscopic group.3
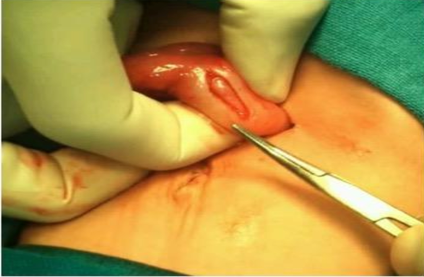
Figure 4. Open pyloromyotomy6
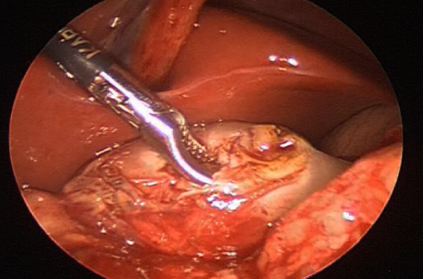
Figure 5. Laparoscopic pyloromyotomy7
Anesthetic Considerations
Preoperative Evaluation
- The patient should be evaluated for dehydration, electrolyte, and acid-base disturbances.1-5
- A history of projectile vomiting, strong appetite, and decreased urine output (four or fewer wet diapers daily suggest dehydration) should be elicited.1-5
- The physical examination should include an examination of mucous membranes and skin turgor to assess hydration.3
Intraoperative
- Gastric outlet obstruction and gastric fluid retention in pyloric stenosis increase aspiration risk.2-3
- An orogastric or nasogastric tube should be inserted prior to induction to decompress the gastric contents and minimize aspiration risk. Often, the stomach is suctioned in multiple positions- supine, left, and right lateral decubitus positions.1,2,4,5
- Gastric ultrasound has been studied and shown to easily confirm an empty stomach. However, results have not been correlated to the risk of aspiration.2,5
- General endotracheal anesthesia should be conducted to minimize aspiration risk.1-3
- Standard American Society of Anesthesiologists monitors should be used.2-3
- An intravenous induction is commonly performed with propofol or ketamine and succinylcholine or rocuronium.1-3
- Rapid sequence induction and intubation (RSII) are often used for pyloromyotomy.1,2,4,5
- RSII may cause a faster onset of hypoxemia as infants have increased oxygen demand and decreased functional residual capacity.
- The use of cricoid pressure is controversial as the correct application of cricoid pressures in infants is difficult, and incorrect application may compress the infant’s airway and hinder intubation.
- Some practitioners use a modified RSII with low-pressure ventilation, targeting peak pressures less than 10-12 cm H2O with avoidance of cricoid pressure.
- Inhalational induction after gastric decompression has also been described.2
- Maintenance of anesthesia is typically with volatile anesthetics in a mixture of oxygen and air.1,2,4,5
- Total anesthesia may be used based on the clinician’s preference and patient characteristics.
- Nitrous oxide is avoided to prevent bowel gas expansion.
- Opioids are either avoided or only short-acting opioids are used as they may increase apnea, delay feeding, and prolong postoperative hospital stay.
- Analgesia is typically achieved with acetaminophen and local anesthetic infiltration by the surgeon. Regional anesthesia blocks, such as ultrasound-guided rectus sheath or transverse abdominus plane blocks, may also be considered.
- Toward the end of the procedure, the surgery may request insufflation of air through the orogastric or nasogastric tube to confirm an intact mucosa at the pylorus.
- The patient should be extubated when fully awake and meeting extubation criteria.
Postoperative
- Postoperative apnea monitoring should be continued for 12-24 hours as these patients are at an increased risk for postoperative apnea.1-5
- Feeding is typically resumed a few hours after surgery based on local practices.3
References
- Kamata M, Cartabuke RS, Tobias JD. Perioperative care of infants with pyloric stenosis. Paediatr Anaesth. 2015; 25 (12):1193-206. PubMed
- Craig R, Deeley A. Anaesthesia for pyloromyotomy. BJA Educ. 2018; 18(6): 173-177. PubMed
- Endom E, Dorfman SR, Olivé AP. Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2024. Accessed April 30th, 2024. Link
- Chung HK. Pyloric stenosis. In: Aglio L, Urman R. (eds) Anesthesiology. Springer, Cham; 2017: 427-434.
- Ko RR. Anesthesia for pyloromyotomy in infants. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2024. Accessed April 30th, 2024. Link
- Jawade KS, Muqtadir A, Jadhav S, et al. Congenital hypertrophic pyloric stenosis at a tertiary care hospital: A surgical experience with 30 infants. Journal of Medical Science and Clinical Research. 2017; 5(9): 27948-56. Link
- Pogorelić Z, Zelić A, Jukić M, et al. The safety and effectiveness of laparoscopic pyloromyotomy using 3-mm electrocautery hook versus open surgery for treatment of hypertrophic pyloric stenosis in infants. Children. 2021; 8(8):701. Link
Other References
- Vlassakova BG. Pyloric stenosis. OA/SPA Pediatric Podcast of the Month. February 2017. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.