Copy link
Methemoglobinemia
Last updated: 05/23/2023
Key Points
- Methemoglobin (MetHb) has the same absorption coefficient at both red and infrared wavelengths. The resulting 1:1 absorption ratio corresponds to a pulse oximetry oxygen saturation (SpO2) reading of 85%.
- Methemoglobinemia is diagnosed with co-oximetry and can be caused by several drugs including prilocaine, benzocaine, nitrites, nitroprusside, and nitroglycerin.
- Methylene blue is an effective treatment for methemoglobinemia unless the patient has G6PD deficiency, in which case vitamin C should be used.
Introduction
- Methemoglobinemia is a state in which the ferrous (Fe2+) irons of heme within Hb are oxidized to the ferric (Fe3+) state. These ferric hemes are then unable to bind O2. As a result, the oxygen-dissociation curve is shifted toward the left, making it more difficult to release O2.1-4
- In the normal state, when hemoglobin binds oxygen, it transfers an electron from the iron to oxygen and the oxygen resembles a superoxide. Subsequent deoxygenation returns the electron to the iron. If the electron is not returned, MetHb is formed. Normally, erythrocytes maintain MetHb levels at less than 1% via the MetHb reductase enzyme system.1
- MetHb has the same absorption coefficient at both red and infrared wavelengths. The resulting 1:1 absorption ratio corresponds to a SpO2 reading of 85% on pulse oximetry. Thus, methemoglobinemia causes a falsely low saturation reading when the arterial oxygen saturation (SaO2) is greater than 85%, and a falsely high reading if the SaO2 is less than 85%.2
Causes
There are two types of methemoglobinemia: congenital and acquired.1,2,4
- Congenital methemoglobinemia is relatively rare and can occur due to:
- Inherited defect or deficiency in nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NADH)-dependent MetHb reductase which enzymatically reduces MetHb back to functional Hb
- Infants generally have lower levels of MetHb reductase in their erythrocytes and manifest greater susceptibility to oxidizing agents.1
- Globin chain mutations favoring the formation of MetHb
- Acquired: Secondary to drugs that oxidize Hb to MetHb at a rate that exceeds the capacity of MetHb reductase system. Drugs that can cause methemoglobinemia include:
- Prilocaine is metabolized by the liver to o-toluidine which oxidizes hemoglobin. Can cause dose-dependent (10mg/kg or >600mg) methemoglobinemia.2,3
- Benzocaine, a common ingredient in topical local anesthetic sprays, can also cause dangerous levels of methemoglobinemia in a dose-independent fashion.2,3
- Nitrates
- Sulfonamides
- Dapsone: common cause for methemoglobinemia
- Phenytoin
- Metoclopramide
- Aniline dye
- Antimalarials like chloroquine or primaquine
Signs and Symptoms
- Clinical evidence of cyanosis despite normal PaO2 and pulse oximetry in the 80s is suggestive of methemoglobinemia.
- The blood of a patient with methemoglobinemia is chocolate brown in color as opposed to cherry red color from carboxyhemoglobin or green color from sulfhemoglobin.4
- In a patient with methemoglobinemia, the degree of cyanosis depends on the total amount of MetHb (total Hb x percent MetHb = total MetHb) and not just the percent of MetHb.4
- Total MetHb > 1.5 g/dL causes cyanosis.4
- For example, a patient with a Hb of 10 g/dL and 10% MetHb will have a total MetHb of 1 g/dL and will not be cyanotic. On the other hand, a patient with a Hb of 18 g/dL with the same 10% MetHb will have a total MetHb of 1.8 g/dL and will be cyanotic.
- Patients with abnormal MetHb levels are usually asymptomatic until the MetHb levels exceed 20% of total Hb.4
- MetHb levels between 20 and 50% cause mild to moderate symptoms of hypoxemia, while levels between 50 and 70% cause severe symptoms (Table 1).4
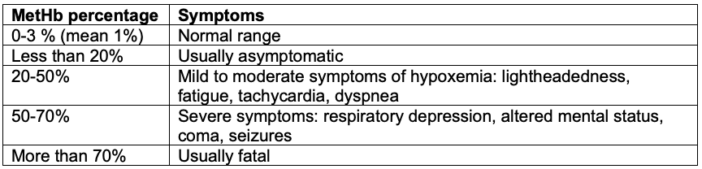
Table 1. Clinical presentation of methemoglobinemia. Adapted from Prchal JT. Methemoglobinemia. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2023. Accessed March 18th, 2023. Link.
Diagnosis
- The diagnosis is confirmed by direct measurement of MetHb by a multiple wavelength co-oximeter. Pulse oximetry is not reliable and will typically read in the mid-80s despite a normal to high PaO2 reading on arterial blood gas.
Treatment
- Treatment should be initiated in symptomatic patients or when the MetHb level is greater than 30%.4
- The definitive treatment of methemoglobinemia is the administration of methylene blue 1-2 mg/kg intravenous over 5 minutes. The dose can be repeated in an hour after the initial dose.1
- Methylene blue acts as an electron donor reducing oxidized Hb.
- Doses above 7-8 mg/kg and rapid administration of methylene blue can paradoxically case oxidation of Hb to MetHb.1
- Rebound methemoglobinemia can occur within 18 hours, as lipid-soluble agents (e.g., benzocaine) are slowly released. Therefore, serial measurements of MetHb should be performed.
- The action of methylene blue as an electron donor requires the activity of the enzyme glucose-6 pyruvate dehydrogenase (G-6PD). The administration of methylene blue in patients with G6PD deficiency can cause hemolysis. Therefore, methemoglobinemia in these patients should be treated with vitamin C (2 mg/kg IV). An exchange transfusion may be required.1
- Methylene blue can also precipitate serotonin syndrome in patients taking selective serotonins reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs) and should be avoided in these patients.4
- Other treatments for refractory methemoglobinemia includes hyperbaric oxygen therapy and red blood cell transfusion.1,4
Anesthetic Considerations
Anesthetic management of a patient with methemoglobinemia includes the following:1
- Hypoxia should be avoided and acidosis should be corrected.
- Arterial line placement should be considered for continuous hemodynamic monitoring, serial arterial blood gases, and measurement of MetHb levels.
- EKG should be monitored for ischemia.
- Drugs likely to cause methemoglobinemia should be avoided (see above).
References
- Oprea AD. Hematologic disorders. In: Hines RL, Marschall KE (eds). Stoelting’s Anesthesia and Co-Existing Disease. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA. Elsevier; 2018:486.
- Butterworth JF, Mackey DC, Wasnick JD, Morgan GE, Mikhail MS (eds). Morgan & Mikhail’s Clinical Anesthesiology. McGraw-Hill Education; 2018:216-217,462-463.
- James S, Teig M, Tremper K. Anesthetic monitoring. In: Pardo M, Miller RD (eds). Basics of Anesthesia. 7th ed. Philadelphia, PA. Elsevier; 2018: 337-62.
- Prchal JT. Methemoglobinemia. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2023. Accessed March 18th, 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.