Copy link
Ketamine
Last updated: 05/09/2023
Key Points
- A phencyclidine derivative, ketamine, induces unconsciousness and analgesia by noncompetitive inhibition of N-methyl-D-aspartate receptors in the brain and spinal cord, respectively.
- Patients with ketamine-induced “dissociative anesthesia” appear awake and maintain certain reflexes but have profound analgesia.
- The primary systemic effects of ketamine relate to its sympathomimetic properties. Increases in heart rate and blood pressure are advantageous for the induction of hemodynamically unstable patients. Bronchodilation is helpful for asthmatics and patients with reactive airway disease.
- Ketamine has multiple routes of administration: intravenous, intramuscular, intranasal, oral, and rectal. A wide range of clinical uses include induction and maintenance of general anesthesia, sedation, and acute and chronic pain management.
- One prominent adverse effect of ketamine is the potential for emergence delirium involving auditory, visual, or proprioceptive hallucinations.
Pharmacology
- Ketamine is a phencyclidine derivative that produces a unique dissociative anesthetic (cataleptic) state rather than a global depression of the central nervous system (CNS).1,2
- Ketamine is generally supplied as a racemic mixture R(-) and S(+) isomers. The S(+) isomer possesses a faster clearance rate and 3-4 times the analgesic activity.1
- It is highly lipid soluble with a redistribution half-life of 11-16 minutes. Similarly, its high clearance rate of 890-1227 mL/min contributes to a relatively short elimination half-life of 2-3 hours.1
- Ketamine is metabolized in the liver via multiple cytochrome P450 isoenzymes principally to norketamine, which has 1/3rd to 1/5th the potency of its parent compound and is renally cleared.1,2
- Ketamine can be administered via numerous routes with variable bioavailability and onset times outlined below: 1,3,4,6
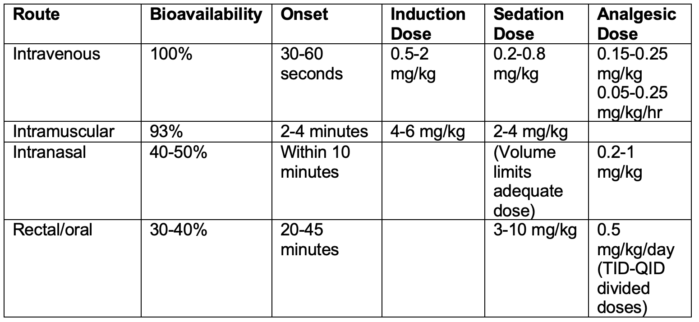
Table 1.
- Ketamine’s anesthetic and analgesic action is likely related to noncompetitive antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors in the cortex, limbic system, and hippocampus.3
- It has variable interactions with mu, delta, and kappa opioid receptors (although this activity is not thought to relate to its analgesic effect) as well as CNS muscarinic and nicotinic receptors.3
Systemic Effects
Central Nervous System
- The “dissociative anesthetic” state induced by ketamine is characterized by a patient who may appear awake.1
- Cough, swallow, and corneal reflexes are maintained but are not necessarily protective.
- Profound analgesia is accompanied by a lack of recall.
- Ketamine increases intracranial pressure by increasing cerebral blood flow (CBF). Cerebral metabolic rate of oxygen (CMRO2) rises and is mirrored by increased CBF. Ketamine has traditionally been avoided in the setting of increased intracranial pressures (ICP).
- The relationship of cerebral blood flow and carbon dioxide is preserved; increases in ICP can be attenuated by hyperventilation, and thus, its role in the setting of increased ICP is being re-examined.1
- Ketamine causes a characteristic lateral-gaze nystagmus.1
- Administration of ketamine results in characteristic electroencephalogram changes:
- Loss of alpha waves
- Significant increase in theta wave activity
- At high enough doses, ketamine can produce burst suppression.2
- Newer evidence suggests that ketamine may serve a neuroprotective role, likely due to its NMDA antagonism. However, this role has not been well established nor the mechanism elucidated.2
- Ketamine causes an increase in intraocular pressure.1
- It does not lower the seizure threshold and is thought to possess anticonvulsant activity.2
- Ketamine increases the cortical amplitude of somatosensory evoked potentials but decreases auditory and visual evoked potentials.2
Cardiovascular System
- Sympathomimetic effect resulting in systemic catecholamine release, inhibition of peripheral norepinephrine reuptake, and vagal suppression.
- Heart rate, blood pressure, and cardiac output are increased.2
- Increases in pulmonary vascular resistance necessitates cautious use in patients with pre-existing right heart strain.3
- Direct negative inotropic effects are induced, which may be clinically evident in a catecholamine-depleted patient.1
Respiratory System
- Spontaneous ventilation is generally preserved, though mild respiratory depression may occur transiently (up to 3 minutes) following administration. Rarely apnea can occur with rapid, large intravenous (IV) doses.2
- Ketamine preserves upper airway reflexes.2
- It increases salivary as well as tracheobronchial secretions and is therefore, often administered with an antisialagogue to minimize this effect.
- Potent bronchodilatory effects are produced by bronchial smooth muscle relaxation.1
- Pulmonary compliance improves in patients with reactive airway disease.
- Ketamine is useful to treat acute bronchospasm.
Clinical Uses
Induction and Maintenance of General Anesthesia
- The sympathomimetic and cardiovascular profile make ketamine a good option for the induction of general anesthesia in hemodynamically unstable patients. However, its chronotropic activity can limit its utility in patients unable to tolerate sudden increases in heart rate (e.g., severe aortic stenosis, severe coronary artery disease).3
- Ketamine’s unique dissociative anesthetic state and intrinsic analgesic properties allow it to function as both an induction and primary anesthetic agent.
- Ketamine preserves skeletal muscle function and is, therefore, unsuitable as a sole anesthetic agent for surgical cases requiring skeletal muscle relaxation.
Acute Pain Management
- Ketamine is a well-established adjunct in the management of acute postoperative pain. It is most beneficial when given both as a bolus prior to incision and then continued as an infusion postoperatively.3
- Small doses (20-60 mg) of ketamine decrease postoperative opioid use and, thereby opioid-related adverse effects.1
- Ketamine provides significant analgesia at subanesthetic blood concentrations.3
- It is especially useful in patients with opiate tolerance and high baseline opiate requirements.
- Ketamine’s analgesic mechanism of action is not fully understood; however, it is thought to result from NMDA antagonism resulting in attenuation of hyperalgesia and CNS sensitization that occur in the setting of acute pain.3
Chronic Pain Management
- The NMDA antagonism central to ketamine’s activity has been identified in preventing hyperalgesia, and as such, it has been shown to provide benefit in the management of certain chronic pain syndromes, most notably chronic regional pain syndrome (CRPS). In this patient population, ketamine administration results in decreases in both pain scores and opiate consumption.3
- Ketamine’s role in chronic pain management is limited by a lack of long-term sustained improvement in pain and by CNS side effects.3
Sedation
- Ketamine is frequently used for procedural sedation, especially in situations in which preservation of upper airway reflexes and spontaneous ventilation is desirable, such as Non-Operating Room Anesthesia (NORA) settings.
- It is especially useful for sedation in the setting of repetitive painful procedures, such as burn dressing changes, where it provides the added benefit of antihyperalgesic properties.3
- It is often used in conjunction with a benzodiazepine (to mitigate psychological side effects) and glycopyrrolate (for its antisialagogue properties).1
Side/Adverse Effects
- Ketamine’s primary adverse effect is emergence delirium, which can be associated with hallucinations (visual, auditory, or proprioceptive) and can occur up to 24 hours after administration. The incidence of emergence delirium varies widely and ranges from 5-30%. Factors associated with increased risk of emergence delirium include:2
- Patients older than 15 years
- Doses greater than 2mg/kg IV
- Female gender
- History of personality disorders
- History of frequent dreaming
- Ketamine inhibits platelet aggregation, and this may be a potential consideration in patients with known coagulopathy.2
- Ketamine is generally avoided in the setting of pheochromocytoma due to its inherent sympathomimetic effects.5
References
- Vuyl J, Sitsen E, Reekers M. Intravenous anesthetics In: Gropper MA et al. Miller’s Anesthesia. 9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier; 2020:661-66.
- Rathmell JP, Dahan A. Intravenous sedatives and hypnotics. In: Flood P, Rathmell JP, Urman RD. Stoelting’s Pharmacology & Physiology in Anesthetic Practice. 6th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2022:176-84.
- Abola R, Geralemou S, Szafran M, Gan et al. Intravenous anesthetics. In: Barash PG, Cullen BF, Stoelting RK, et al. Clinical Anesthesia. 8th edition. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer; 2017:49-97.
- Carr DB, Goudas LC, Denman WT, et al. Safety and efficacy of intranasal ketamine for the treatment of breakthrough pain in patients with chronic pain: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover study. Pain. 2004;108(1):17-27. PubMed
- Ramakrishna H. Pheochromocytoma resection: Current concepts in anesthetic management. J Anaesthesiol Clin Pharmacol. 2015;31(3):317-23. PubMed
- Ketamine. Lexicomp. Accessed 23 April 2023. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.