Copy link
Hypocalcemia
Last updated: 04/30/2025
Key Points
- Hypocalcemia can be caused by parathyroid hormone (PTH) or Vitamin D deficiency, affecting muscle contraction, heart function, and bone strength.
- Symptoms range from tingling and muscle cramps to seizures and prolonged QT, with classic signs like Trousseau and Chvostek.
- Management depends on severity, with oral calcium for mild cases, intravenous (IV) calcium for severe cases, and careful anesthetic planning due to increased neuromuscular excitability and risk of laryngospasm.
Calcium Regulation & Hypocalcemia
- Calcium participates in various biochemical processes and is critical for heart function, bone strength, muscle contraction, and as a signaling molecule.1
- Calcium is regulated by three key hormones, including1
- PTH
- 1,25-dihydroxy Vitamin D3 (Vitamin D3)
- Calcitonin
- When serum calcium levels drop, the parathyroid glands secrete PTH, which enhances calcium reabsorption in the kidneys. PTH also stimulates the kidneys to produce Vitamin D3, promoting absorption in the intestines. Additionally, PTH activates osteoclasts, which break down bone to release calcium into the bloodstream (Figure 1).1,2
- When serum calcium levels increase, calcitonin is secreted by thyroid parafollicular cells and reduces calcium levels by stimulating osteoblast activity, promoting calcium deposition into bone. Calcitonin also inhibits calcium reabsorption in the kidneys, increasing excretion in urine, and reduces intestinal calcium absorption (Figure 1).1,2

Figure 1. Hormonal Regulation of Calcium Homeostasis; Source: Wikimedia Commons. Originally by Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Website. CC BY 3.0.
Hypocalcemia
- The normal reference range for total serum calcium is 8.5 to 10.5 mg/dL.1
- Calcium also exists in its ionized (biologically active) form, which ranges from 4.65 to 5.25 mg/dL.1
- Values below these thresholds indicate hypocalcemia.
Causes & Clinical Presentation of Hypocalcemia
Hypocalcemia can result from: PTH deficiency, elevated PTH levels, and other causes (Table 1).1,3
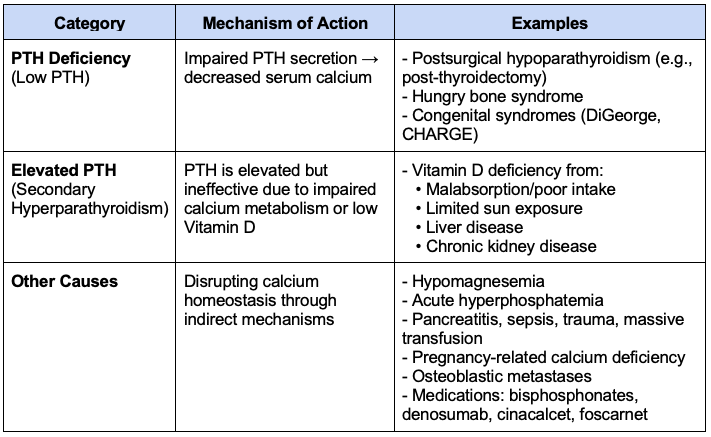
Table 1. Causes of hypocalcemia
Clinical Presentation
- The clinical manifestations of hypocalcemia can vary from no symptoms to severe, life-threatening complications such as seizures or heart failure.1,3
- Tetany, resulting from a rapid drop in ionized calcium, is concerning and associated with respiratory alkalosis.1,3
- Patients may also report “pins and needles” sensations around the mouth and extremities.3
- Less common are psychiatric symptoms such as anxiety, depression, or mood instability.1,3
- Two classic physical signs of hypocalcemia include:
- Trousseau sign → spasm induced by inflating a blood pressure cuff3,4
- Chvostek sign → tapping of the facial nerve causes facial muscle twitching3,4
- Prolonged QT on electrocardiogram (ECG) another important finding, as it increases the risk of torsades de pointes, a potentially fatal arrhythmia (Figure 2).1,3
- T-wave flattening may also be seen in some cases.3
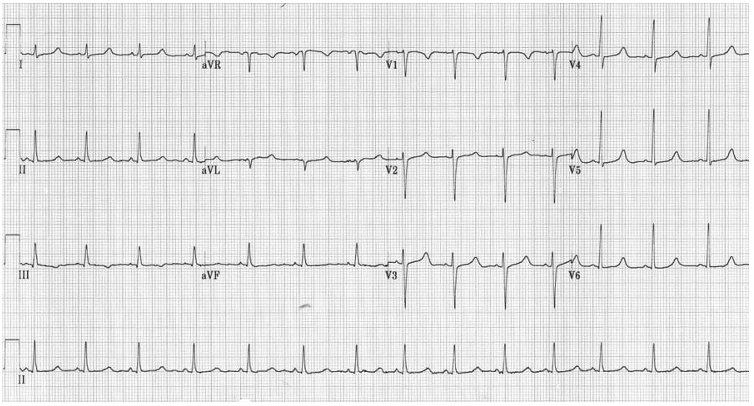
Figure 2. Electrocardiogram showing QT interval prolongation in hypocalcemia. Source: Life in the Fast Lane ECG Library. Link
Treatment & Anesthetic Consideration in Hypocalcemia
Management depends on symptom severity, calcium levels, and underlying cause.
- Oral calcium is given when hypocalcemia is mild.1,4
- There are two common types of oral calcium:
1. Calcium carbonate → contains 40% elemental calcium1,4
2. Calcium citrate → contains 21% elemental calcium1 - The goal is to provide 1.5 – 2 g of elemental calcium/day, split into three doses.4
- Calcium carbonate needs acid in the stomach to be absorbed; therefore, calcium citrate is preferred for patients taking proton pump inhibitors.1
- Vitamin D is usually given alongside to help absorb calcium.1,4
- There are two common types of oral calcium:
- Intravenous calcium is used for severe symptoms (i.e., seizures, tetany, or heart issues), prolonged QT, or if their calcium drops quickly.1
- There are two types of IV calcium:
1. Calcium gluconate → preferred1,4
2. Calcium chloride → stronger but can cause tissue necrosis4
- There are two types of IV calcium:
- Recombinant human PTH is approved to treat hypocalcemia.1
- Chronic hypoparathyroidism
- Genetic conditions that cause low PTH levels
- Disease-specific treatment:
- Postsurgical hypoparathyroidism → prophylactic calcium and taper1,4
- Hypomagnesemia → magnesium must be corrected before calcium4
- Vitamin D deficiency → correct Vitamin D before calcium1,4
- CKD → treat with active Vitamin D (e.g., calcitriol)1
Anesthetic Considerations
- Hypocalcemia can be worsened by low albumin, respiratory alkalosis, massive transfusions (citrate binding), and cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB).5
- Volatile anesthetics (e.g., halothane, enflurane) act as nonspecific calcium antagonists and may exacerbate the cardiovascular effects of hypocalcemia (i.e., myocardial contractility, prolonged QT interval, and bradyarrhythmias).5
- Increased neuromuscular excitability may potentiate nondepolarizing neuromuscular blockers with hypocalcemia, resulting in prolonged paralysis.5
- Succinylcholine may also alter calcium dynamics via fasciculations.5
- Laryngospasm can occur after neck surgery due to low calcium levels, and urgent calcium replacement may be needed to stop symptoms.1,3-5
- Bupivacaine’s cardiotoxic effects may be enhanced in hypocalcemia due to increased inhibition of calcium channels.5
- Caution is advised with high doses.5
- Alkalosis (due to hyperventilation) increases calcium binding to albumin, reducing ionized calcium.5
- Respiratory status should be carefully managed.4,5
- During CPB, factors like citrated blood, fluid dilution, and low-protein solutions can lower active calcium levels; therefore, monitoring and correcting calcium are essential.3,5
Citrate Toxicity in Blood Transfusion
- Citrate is an anticoagulant commonly used in stored blood products.6 Each 450 mL unit of blood contains 9-10 mmol of citrate. Under normal circumstances, it is metabolized by the liver.6 Massive transfusion leads to infusion of a large amount of citrate. In patients with impaired hepatic function, citrate can accumulate in the bloodstream.6,7
- Citrate binds to ionized calcium, leading to or worsening hypocalcemia.6,7
- This can result in myocardial depression and coagulopathy.6,7
- Hypocalcemia in the context of massive transfusion is associated with increased risk of mortality, longer ICU stays, and additional transfusion requirements.7
- Management in this setting requires slow transfusion to allow for citrate metabolism and monitoring of ionized calcium levels and QT interval on ECG.6
- Most patients do not require calcium administration. However, calcium chloride or gluconate should be administered to patients with symptomatic hypocalcemia.6
References
- Goyal A, Anastasopoulou C, Ngu M, et al. Hypocalcemia. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island, FL: StatPearls Publishing; 2025. Accessed March 23, 2025. Link
- Babić Leko M, Pleić N, Gunjača I, Zemunik T. Environmental factors that affect parathyroid hormone and calcitonin levels. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(1):44. PubMed
- Schafer AL, Shoback DM. Hypocalcemia: diagnosis and treatment. In: Feingold KR, Ahmed SF, Anawalt B, et al., eds. Endotext. South Dartmouth, MA: MDText.com, Inc.; 2000–. Updated January 3, 2016. Accessed March 23, 2025. Link
- Fong J, Khan A. Hypocalcemia: updates in diagnosis and management for primary care. Can Fam Physician. 2012;58(2):158-62. PubMed
- Aguilera IM, Vaughan RS. Calcium and the anaesthetist. Anaesthesia. 2000;55(8):779-90. PubMed
- Hess JR. Massive blood transfusion. In: Post T(ed). UpToDate. 2025. Link
- Schriner JB, Van Gent JM, Meledeo MA, et al. Impact of transfused citrate on pathophysiology in massive transfusion. Crit Care Explor. 2023;5(6):e0925. Link
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.