Copy link
Inhaled Anesthetic Agents: Mechanism of Action, Uptake, and Distribution
Last updated: 03/28/2023
Key Points
- The clinical effects of inhalational anesthetics are determined by the agent’s partial pressures in the brain, which reach equilibrium with the alveoli and blood upon induction.
- Induction occurs faster with increased delivery and decreased uptake of anesthetics.
- Anesthetic uptake is determined by anesthetic solubility in the blood, alveolar blood flow, and the difference in partial pressures between alveolar gas and venous blood.
- Minimal alveolar concentration is a measure of the clinical effect of anesthetics and correlates with the potency of each anesthetic agent.
Mechanism of Action
Halogenated hydrocarbon volatile anesthetics (sevoflurane, isoflurane, desflurane) and nitrous oxide are the most commonly used inhaled anesthetic agents today.
Mechanism
- Inhaled anesthetics act through multiple complex mechanisms and pathways within the central nervous system (CNS).
- The agents act by binding to target sites in proteins to enhance inhibitory receptors (gamma-amino butyric acid, glycine) and suppress excitatory transmission (block the action of glutamate at N-methyl D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors).1
- Hypnosis/sedation and amnesia are produced through effect sites in the brain. Immobility is produced by actions within the spinal cord.
- Lipid solubility correlates to anesthetic potency (Meyer-Overton correlation).
- There is currently no comprehensive theory of volatile anesthetics, and our understanding of the sequence of events, networks, and mechanisms is limited.
- Nitrous oxide is an inhaled anesthetic that works primarily by NMDA receptor antagonism.2
Properties of Gases
- The partial pressure of a gas is the fraction of the mixture that the agent comprises.
- The partial pressure is directly proportional to tissue concentration which determines its clinical effect.
- Inhaled anesthetics function by achieving optimal and constant partial pressure at the CNS effect site (brain, spinal cord).
- Equilibrium between alveolar partial pressures (PA) and arterial blood (Pa) results in steady-state partial pressures in the brain.3
-
- PA (Pbrain) = input (delivery) – uptake (into pulmonary circulation)
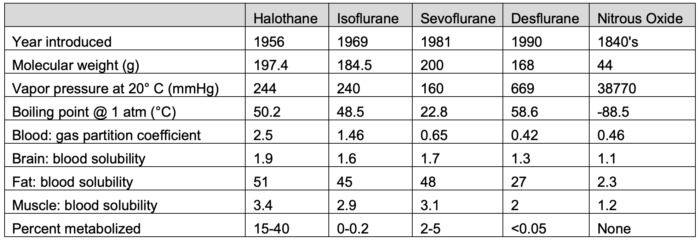
Table 1. Properties of common inhaled anesthetic agents. Adapted from Forman SA, Ishizawa Y. Inhaled anesthetic uptake, distribution, metabolism, and toxicity. In: Miller RD, Gropper MA, et al. Miller's Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA 9th ed. Elsevier. 2019: 509-539.
Uptake & Distribution (Pharmacokinetics)
Fi = concentration of inspired anesthetic in delivered gas flows
FA = alveolar concentration
FA/Fi = The rate of rise of concentration which determines the speed of inhalational induction
- An increased FA/Fi results in faster induction.
Factors Affecting Anesthetic Delivery
1. Inspired concentration (Fi)
-
- Increasing the concentration of the inhaled anesthetic increases FA, but also the rate of rise of FA/Fi via the concentration effect and the second gas effect (see below).
2. Alveolar ventilation
-
- ↑ ventilation can counter uptake into circulation.
- The effect is greater with soluble agents, which are subject to greater uptake.
- Less pronounced with insoluble agents, where FA/Fi quickly reaches 1.0.
3. Characteristics of anesthesia circuit
-
- Circuit volume: ↓ delivery with h volume.
- Gas flow: ↑ delivery with ↑ flow.
- Solubility of agent into system components: ↓ delivery with ↑ absorption.
4. Characteristics of pulmonary system
-
- Functional residual capacity (FRC): increased FRC will dilute the inspired gas due to a larger gas reservoir.
- Larger FRC → slower induction.
- V/Q mismatch: see below.
- Functional residual capacity (FRC): increased FRC will dilute the inspired gas due to a larger gas reservoir.
- Concentration effect
- When the inhaled anesthetic represents a large fraction of the inhaled gas mixture, its rapid uptake results in a smaller relative anesthetic concentration drop, because the volume of the alveolar gas also decreases.5
- This is only clinically relevant with nitrous oxide since it is used in high concentrations.
- Second-gas effect
- The higher concentration of one inhaled anesthetic (usually nitrous oxide) will accelerate the increase in alveolar concentration of a coadministered inhaled agent.5
Uptake
- Uptake by the body (via the pulmonary circulation) delays the increase in FA.
- The greater the uptake, the slower the rise in FA/Fi.
- The three primary determinants of uptake include:
1. Solubility in blood:
- Expressed as blood: gas coefficient.
- A more soluble anesthetic will have a higher blood: gas coefficient.
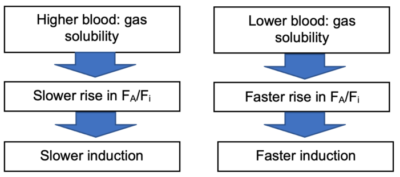
2. Alveolar blood flow: if there is no pulmonary shunting, alveolar blood flow is equal to the cardiac output (CO).
- Increase in CO → more rapid uptake of agent → slower rise in FA/Fi.
- Low CO → less uptake → ↑ rise in FA/Fi → quicker induction.
- Change in CO has a more pronounced effect on soluble anesthetics, where uptake is greater.
- Note: as cerebral blood flow is well regulated, increasing CO will primarily deliver the anesthetic agent to other tissue sites.
3. The difference in partial pressures between alveoli and venous blood (PA – Pv)
- Anesthetic flows across the alveolar-capillary interface are driven by the gradient in partial pressures. The net flow reverses during anesthetic elimination.
- The larger the gradient, the greater the uptake into circulation.
- Primarily determined by tissue uptake (see “Distribution” below).
- As soluble agents are taken up in tissues, venous partial pressure is initially low → increasing uptake → slowing the rise in FA/Fi.
- As tissue partial pressure approaches alveolar partial pressure, gradient will decrease → slowing the rate of uptake.
Inhalational Induction in Infants and Young Children
- The rapid wash-in (rise in FA/Fi) of inhaled anesthetics in infants and young children can be explained by the following.4
- Greater alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio (VA/FRC ratio).
- VA/FRC ratio is approximately 5:1 in neonates compared to only 1.5:1 in adults.
- Greater impact on more soluble agents (halothane)
- Greater fraction of the cardiac output is distributed to the vessel-rich group (VRG).
- VRG comprises approximately 18% of body weight in neonates compared to 8% in adults.
- Reduced tissue/blood solubility
- Tissue/gas solubilities of inhaled anesthetics in the VRG in neonates is approximately one-half those in adults.
- It is explained by greater water content and decreased protein and lipid concentrations.
- Reduced blood/gas solubility
- Blood solubility of more soluble inhaled agents is about 18% less in neonates.
- It is explained by decreased serum cholesterol and proteins (including albumin).
- However, blood solubility of sevoflurane is similar in neonates and adults.
- Greater alveolar ventilation to FRC ratio (VA/FRC ratio).
Effect of V/Q Mismatch on FA/Fi
- Pulmonary dead space:
- Increased dead space reduces effective alveolar ventilation, slowing induction.
- Greater impact on less-soluble agents, where the limiting factor is alveolar ventilation.
- Shunt:
- R → L (transpulmonary or intracardiac, i.e., one-lung ventilation, VSD):
- Increases alveolar-arterial difference (↑ PA and ↓ Pa), slowing induction5
- Greater impact on less-soluble agents
- L → R:
- Minimal effect on the speed of induction with inhaled anesthetics
- R → L (transpulmonary or intracardiac, i.e., one-lung ventilation, VSD):
Distribution
- Multicompartment model due to differing rates of uptake by tissue.
- Tissue uptake is determined by tissue solubility (tissue: blood coefficients), tissue perfusion, and partial pressure gradient (Pa: Ptissue).
- Four tissue groups:
1. Vessel-rich group: brain, heart, lungs, kidney, liver, spinal cord
• Rapidly reaches equilibrium (minutes)
2. Muscle:
• Equilibrates over hours
3. Fat:
• ↑ effective volume with soluble drugs
• Slow uptake due to low perfusion and high volume
• Equilibrates over days
4. Vessel-poor group: bone, connective tissues
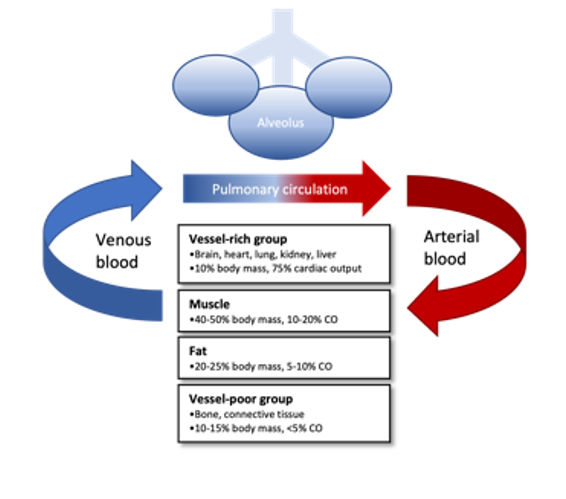
Figure 2. Flow diagram of uptake and distribution of inhaled anesthetics. Anesthetic agents are transferred into pulmonary circulation from the alveoli and then delivered by arterial blood to four main organ compartment groups. The uptake into tissues is determined by the tissue solubility, relative blood flow (cardiac output), and partial pressure gradients. Anesthetic agents then diffuse out of tissues into venous circulation where they are transferred into alveoli and eliminated by the lungs.
Minimal Alveolar Concentration (MAC)
- Definition: the steady-state alveolar concentration of the inhaled anesthetic at which 50% of healthy individuals do not respond to a surgical stimulus.6
- MAC values correspond to the potency of the inhaled anesthetic and vary between agents.
- MAC values are additive between the anesthetic agents.
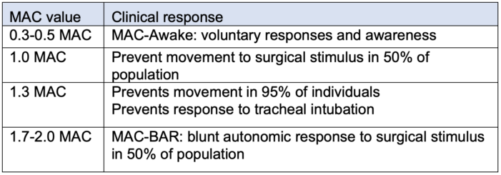
Table 2. Clinically useful minimal alveolar concentration (MAC) values.
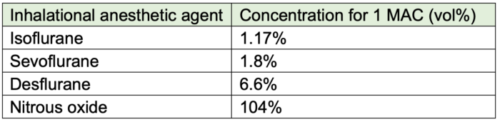
Table 3. Inhalational anesthetic concentration for 1 MAC (Age 40).
Factors Affecting MAC
- Age: MAC increases by 30% from birth until 1-6 months of age and then decreases by 6-7% every decade after 20 years of age.7
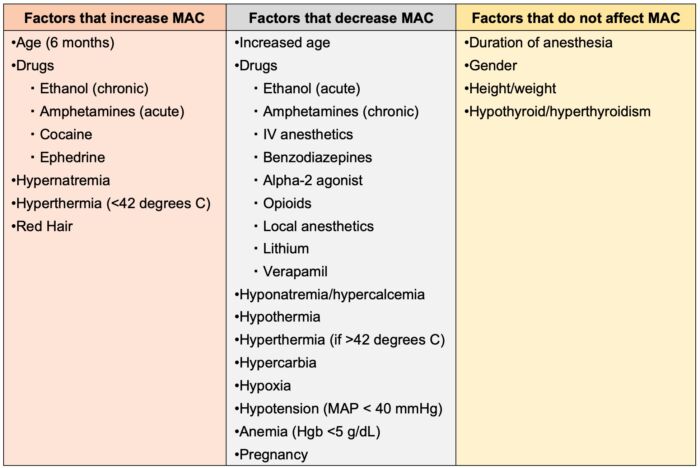
Table 4. Factors that affect minimal alveolar concentration (MAC). Adapted from McKay RE. Inhaled Anesthetics. In: Pardo MC, Miller RD. Basics of Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA 7th ed. Elsevier. 2018: 83-103.
References
- Perouansky M, Pearce RA, Hemmings HC, et al. Inhaled anesthetics: Mechanism of action. In: Gropper M, Cohen NH, Eriksson LI, et al. Miller's Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA 9th ed. Elsevier. 2019: 487-508.
- Jevtović-Todorović V, Todorović SM, Mennerick S, et al. Nitrous oxide (laughing gas) is an NMDA antagonist, neuroprotectant and neurotoxin. Nat Med. 1998;4(4):460-3. PubMed
- Katzung BG, Vanderah TW. eds. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology, 15e. McGraw Hill; 2021.
- Anderson BJ, Lerman J, Coté CJ. Pharmacokinetic and pharmacology of drugs used in children. In: Coté CJ, Lerman J, Anderson BJ (eds) A Practice of Anesthesia for Infants and Children. 6th edition. Philadelphia, PA. Elsevier. 2019: 100-176.
- Forman SA, Ishizawa Y. Inhaled anesthetic uptake, distribution, metabolism, and toxicity. In: Gropper M, Cohen NH, Eriksson LI, et al. Miller's Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA 9th ed. Elsevier. 2019: 509-539.
- Eger EI 2nd, Saidman LJ, Brandstater B. Minimum alveolar anesthetic concentration: a standard of anesthetic potency. Anesthesiology. 1965;26(6):756-63. PubMed
- Hendrickx JFA, De Wolf AM. End-tidal anesthetic concentration: Monitoring, interpretation, and clinical application. Anesthesiology. 2022;136(6):985-96. PubMed
- 8. McKay RE. Inhaled Anesthetics. In: Pardo MC, Miller RD. Basics of Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA 7th ed. Elsevier. 2018: 83-103.
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.