Copy link
Hyperparathyroidism and Parathyroidectomy
Last updated: 09/20/2023
Key Points
- Parathyroidectomy is often performed for symptomatic parathyroid adenomas, where overproduction of serum parathyroid hormone (PTH) leads to symptomatic hypercalcemia.
- During parathyroidectomy, patients are closely monitored using modalities such as a nerve integrity monitor (NIM) endotracheal tube to detect recurrent laryngeal nerve injury, and intraoperative serum PTH levels to ensure successful parathyroid resection.
- Postoperatively, patients are vulnerable to hypocalcemia, which usually peaks within 24-48 hours after the procedure.
Physiology of Calcium Regulation
- Calcium is a critical mineral component of the body.1
- It provides structures to the skeleton and plays a major role in muscle contraction.
- It is a key neurotransmitter and plays an important role in intracellular signaling, blood coagulation, and neuromuscular transmission.
- Ninety-nine percent of the total body calcium is stored in the bone mineral reservoir.1 Fifty-five to 60% is bound to plasma proteins or complexed with phosphate or citrate. The free ionized calcium exerts physiological effects.
- Normal serum calcium levels are 8.6 – 10.4 mg/dL.1 Serum calcium, not ionized calcium, decreases with reduced albumin levels.
- Serum ionized calcium levels are normally maintained within a very narrow range by a tightly regulated calcium-PTH homeostatic system that includes the hormones PTH and calcitonin, and vitamin D (Figure 1).
- When plasma calcium levels are low, PTH is released by the parathyroid glands. PTH acts by promoting reabsorption of calcium by the kidneys and gastrointestinal (GI) tract and stimulating osteoclast proliferation and bone resorption by osteoclasts, thereby releasing calcium from bone. It also increases the conversion to active vitamin D in the kidneys.
- When plasma calcium levels are high, calcitonin is released by the thyroid gland. Calcitonin acts by opposing the effects of PTH, causing decreased bone resorption and decreased calcium reabsorption by the kidneys and intestines.
- Vitamin D maintains calcium homeostasis by increasing absorption of calcium from the intestines and facilitating the bone resorption effects of PTH.
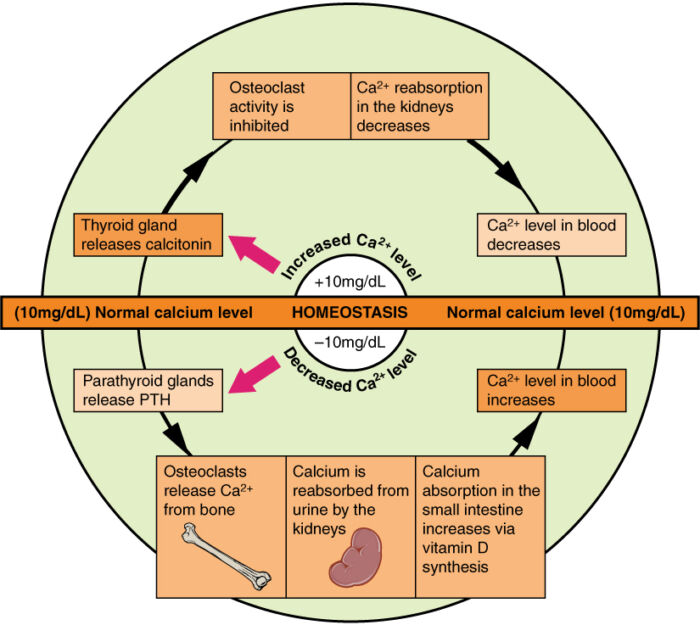
Figure 1. Regulation of plasma calcium homeostasis. Source: Wikimedia Commons. Originally by Anatomy & Physiology, Connexions Website. CC BY 3.0. Link.
Hyperparathyroidism
Hyperparathyroidism is characterized by elevated PTH levels and can be subdivided into multiple types.
- Primary hyperparathyroidism (pHPT)
- Abnormally active PTH secretion → hypercalcemia
- Most commonly caused by parathyroid gland adenoma2
- Secondary hyperparathyroidism (sHPT)
- Reactive hyperplasia of parathyroid gland and increased PTH secretion in response to hypocalcemia or hyperphosphatemia
- Hyperparathyroidism occurs most frequently in setting of chronic kidney disease (CKD).3 Other causes include sarcoidosis, multiple myeloma, vitamin D intoxication, etc.
- Tertiary hyperparathyroidism
- Progression of untreated sHPT → autonomous and refractory secretion of PTH → hypercalcemia3
Clinical Presentation
- The most common clinical presentation of pHPT in the Western world is asymptomatic hypercalcemia detected incidentally during routine biochemical screening.4
- In symptomatic pHPT, the classical signs and symptoms are known as “bones, stones, abdominal moans, and psychic groans” and result from increased PTH levels and hypercalcemia.4
- Nephrolithiasis occurs in 60-70% of patients.
- Skeletal disorders such as osteitis fibrosa cystica, osteopenia and osteoporosis are common secondary to high rates of bone turnover. Patients frequently complain of bone pain, especially in the anterior tibia.
- Some patients experience profound muscle weakness and muscle atrophy.
- GI symptoms include anorexia, nausea, vomiting, and constipation.
- Approximately 1/3rd of patients are hypertensive.
- Polyuria and polydipsia can be present.
- Peptic ulcer disease is more common.
- Neuropsychiatric symptoms such as confusion or depression can be present.
- Cardiac arrhythmias can result from shortened QT interval and prolonged PR interval.
Diagnosis
- As mentioned earlier, pHPT is usually diagnosed after an incidental finding of elevated serum calcium concentrations or nephrolithiasis. In addition to elevated total and ionized calcium levels, the diagnosis of pHPT is confirmed by detecting markedly elevated PTH levels, often in the range of 1.5-2-fold the upper limits of normal.2
- Additional laboratory studies include2
- 24-hour urinary calcium to assess the risk of kidney complications
- Serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D levels to identify patients who require vitamin D repletion
- Serum creatinine levels or estimated glomerular filtration rate to assess kidney function
- Bone mineral density using DEXA scan to look for osteopenia or osteoporosis
- Renal ultrasound to evaluate for nephrolithiasis
Treatment
- All patients with symptomatic pHPT should ideally undergo parathyroidectomy, which is the only definitive therapy.5
- For asymptomatic patients, surgery is indicated if one of the following conditions is met.5
- Serum calcium greater than 1 mg/dL above the upper limit of normal.
- Skeletal BMD T score ≤ 2.5 at lumbar spine, total hip, femoral neck, or distal radius.
- Decreased kidney function: eGFR < 60 mL/min/1.73 m2, high 24-hour urine calcium or presence of nephrolithiasis.
- Age younger than 50 years.
- For asymptomatic patients who don’t meet criteria for surgery or refuse surgery, serum calcium and creatinine levels are monitored annually. Bone density exams are performed every 1-2 years.5
- Medical therapy is indicated for patients who are poor surgical candidates.
- In patients with severe hypercalcemia, cinacalcet, a calcimimetic agent is used. It inhibits PTH release by increasing sensitivity of parathyroid gland to circulating calcium.
- Emergency treatment of severe hypercalcemia (serum concentrations > 15 mg/dL) includes volume expansion with normal saline and diuretics.
- In patients with osteoporosis, bisphosphonates (pamidronate, etidronate, clodronate) are used as potent inhibitors of bone resorption. In patients who don’t tolerate bisphosphonates, denosumab, a human monoclonal antibody, is used as alternative.
- Vitamin D supplementation is recommended in patients with low vitamin D levels.
Surgical Procedure: Parathyroidectomy
- Parathyroidectomy is either performed through a standard bilateral neck exploration or a more focused parathyroid exploration for a solitary parathyroid adenoma.6
- Endoscopic or video-assisted parathyroidectomy has also been proposed.
- A minimally invasive radiation-guided approach through the injection of Tc99m sestamibi, localization with gamma probes, and removal through a small incision has been described.
Anesthetic Considerations for Parathyroidectomy
Preoperative Considerations
- The majority of patients undergoing elective parathyroidectomy are asymptomatic. However, all patients should be evaluated for symptoms of hypercalcemia.7
- Electrolyte levels can be checked with a basal metabolic profile. An electrocardiogram (ECG) may also be ordered to evaluate for cardiac arrythmias resulting from hypercalcemia.
- Therapeutic interventions for preoperative hypercalcemia include the administration of intravenous fluids, diuretics, or bisphosphonates. Patients experiencing nausea secondary to hypercalcemia may be treated with antiemetic medications.
Intraoperative Considerations
- In addition to standard American Society of Anesthesiologists monitors, intraoperative nerve monitoring may be utilized during the procedure due to the risk of injury to the recurrent laryngeal nerve (RLN) during parathyroid surgery.7
- Using a NIM endotracheal tube allows for intraoperative stimulation of the RLN.8 The NIM tube converts laryngeal muscle action potentials into electromyography signals during periods of RLN stimulation. A decrease in waveform amplitude and/or increase in waveform latency may indicate potential RLN injury.
- Avoidance of neuromuscular blockers or utilization of short-acting rather than long-acting neuromuscular blockers allows intraoperative nerve stimulation and monitoring.7
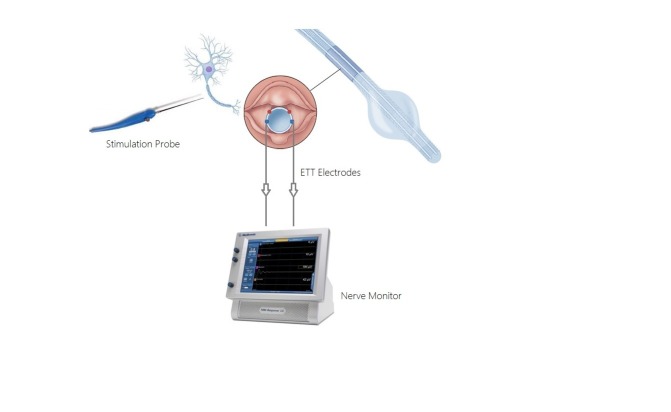
Figure 2. Medtronic XoMed Nerve Integrity Monitor (NIM). Source: Ghani U, et al. Role of intraoperative nerve monitoring during parathyroidectomy to prevent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Cureus. 2016. CC BY.
- In patients experiencing significant nausea secondary to hypercalcemia, it may be beneficial to utilize induction strategies that will mitigate the risk of aspiration such as rapid sequence induction, reverse Trendelenburg positioning, and/or preoperative nasogastric tube if nausea is severe.7
- Confirmation of parathyroid removal can be conducted through the measurement of serum PTH levels during the procedure. PTH levels are typically measured at preincision, pregland removal, and 10 minutes postgland removal. The patient will require frequent blood draws for PTH measurement.7
- Two criteria are utilized to determine if resection is successful:
- 50% decrease in PTH levels from pre-excision baseline within 10 minutes after excision.
- PTH levels that are normal or near normal within 10 minutes after excision.
- If PTH level has decreased significantly, but does not meet the above criteria, another serum PTH may be taken at 20 minutes to evaluate further.9
- It is important to facilitate a smooth emergence with minimal coughing and bucking to avoid agitation of the surgical site and minimize the risk of airway compromise.7
Postoperative Considerations
Hypocalcemia
- After parathyroidectomy, patients are susceptible to hypocalcemia due to a rapid decrease in serum PTH levels post-surgery. The typical calcium nadir occurs 24-48 hours after surgery.6
- Symptoms of hypocalcemia include tetany, paresthesias, perioral numbness, etc. Severe hypocalcemia may result in seizures, laryngospasm or cardiac arrhythmias with ECG changes such as prolonged QT interval.6
- Transient postoperative hypocalcemia is more common in patients with chronic vitamin-D deficiency. These patients may reduce their risk of hypocalcemia by repleting vitamin D preoperatively by taking a regimen of ergocalciferol.
- Severe hypocalcemia may be treated with IV calcium chloride or calcium gluconate.6
Symptomatic Hematoma
- Symptoms of a neck hematoma include respiratory distress, anxiety, dysphagia, pain, etc. On examination, an anterior cervical mass may be noted.6
- Although rare, this complication can result in life-threatening airway compromise.
- Early recognition and emergent surgical decompression are needed in such cases.
Recurrent Laryngeal Nerve Injury
- RLN injury is a rare complication that results in the vocal cords in the paramedian position and the inability to abduct or adduct the vocal cords. Unilateral RLN injury presents with hoarseness or stridor, while bilateral injury can result in life-threatening airway compromise and require reintubation.6
References
- Kiefer J, Mythen M, Roizen MF, et al. Anesthetic implications of concurrent diseases. In: Miller’s Anesthesia. Philadelphia, PA. Elsevier. 2020: 999-1064.
- Fuleihan GE, Silverberg SJ. Primary hyperparathyroidism: Diagnosis, differential diagnosis, and evaluation. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2023. Accessed September 6, 2023. Link
- Saliba W, El-Haddad B. Secondary hyperparathyroidism: pathophysiology and treatment. J Am Board Fam Med. 2009; 22 (5): 574-81. PubMed
- Fuleihan GE, Silverberg SJ. Primary hyperparathyroidism: Clinical manifestations. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2023. Accessed September 6, 2023. Link
- Bilezikian JP, Khan AA, Silverberg SJ, et al. Evaluation and management of primary hyperparathyroidism: Summary statement and guidelines from the Fifth International Workshop. J Bone Miner Res. 2022; 37 (11): 2293-314. PubMed
- Perrier ND, Dickson PV, Figueroa AS. Parathyroid exploration for primary hyperparathyroidism. In: Post T, ed. UpToDate; 2022. Accessed September 6, 2023. Link
- Kazaure H, Lin D, Lorenzo J, Mihm F. Endocrine surgery: Parathyroidectomy. In: Jaffe R, Schmiesing C, Golianu B. Anesthesiologist’s Manual of Surgical Procedures. 6th edition. Philadelphia; Wolters Kluwer; 2020: 753-8.
- Ghani U, Assad S, Assad S. Role of intraoperative nerve monitoring during parathyroidectomy to prevent recurrent laryngeal nerve injury. Cureus. 2016; 8(11): e880 PubMed
- Calò PG, Pisano G, Loi G, et al. Intraoperative parathyroid hormone assay during focused parathyroidectomy: the importance of 20 minutes measurement. BMC Surg. 2013; 13: 36. PubMed
Copyright Information

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.